- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. August 2018
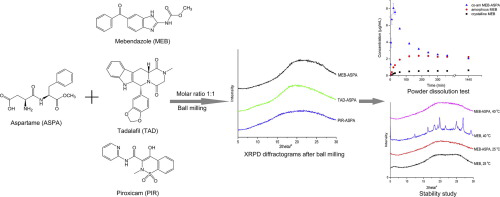
Co-amorphous drug delivery systems are a promising approach to improve the dissolution rate and therefore potentially the oral bioavailability of poorly-water soluble drugs. Several low molecular weight excipients, for instance amino acids, have previously been shown to stabilize the amorphous form and increase the dissolution rate of drugs. In this study, the feasibility of aspartame, a methyl ester of the aspartic acid-phenylalanine dipeptide, as a co-former was investigated and compared with...
27. July 2018
Co-amorphous drug delivery systems are attracting increasing attention in the pharmaceutical field, due to their promising potential to improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. In this study, three organic acids, namely benzoic acid, malic acid and citric acid and , were investigated as co-formers for the weakly basic drug carvedilol. It was hypothesised that the mono-, di- and triprotic nature of the organic acids could result in co-amorphous salt formation...
27. September 2017
Many future drug products will be based on innovative manufacturing solutions, which will increase the need for a thorough understanding of the interplay between drug material properties and processability. In this study, hot melt extrusion of a drug-drug mixture with minimal amount of polymeric excipient was investigated.
05. September 2017
Abstract Amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) are probably the most common and important supersaturating drug delivery systems for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. These delivery systems are able to achieve and maintain a sustained drug supersaturation which enables improvement of the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs by increasing the driving force for drug absorption. However, ASDs often require a high weight percentage of carrier (usually a hydrophilic polymer) to...