- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
27. July 2018
The present study elucidated the advantages of using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose E5 (HPMC) as auxiliary excipient in maintaining storage stability and solubilization ability for curcumin amorphous solid dispersion (Cur ASDs) formulated by Eudragit E100 (E100). Polarized light microscopy and in vitro dissolution experiment was applied for confirming the ability of HPMC on inhibiting crystallization thereby maintaining storage stability in Cur ASDs. Meanwhile, as a non-ionic surfactant, HPMC...
02. June 2018
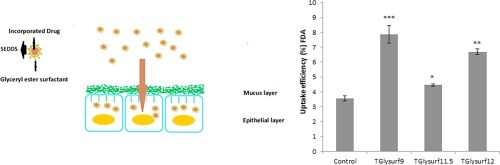
The aim of the study is the evaluation of the impact of glyceryl ester surfactants on cell permeating properties of SEDDS (self-emulsifying drug delivery systems). Methods SEDDS containing the glyceryl ester surfactants polyglyceryl-3-stearate (TGlysurf9), polyglyceryl-5-oleate (TGlysurf11.5) and glyceryl stearate citrate (TGlysurf12) were prepared and characterized regarding droplet size and zeta potential. Toxicity studies were performed on Caco-2 cells using resazuring assay. The...
25. March 2017
Abstract Developing a drug carrier system which could perform targeted and controlled release over a period of time is utmost concern in the pharmaceutical industry. This is more relevant when designing drug carriers for poorly water soluble drug molecules such as curcumin and 6-gingerol. Development of a drug carrier system which could overcome these limitations and perform controlled and targeted drug delivery is beneficial. This study describes a promising approach for the design of novel pH...
17. October 2016
Abstract The present study focused on the preparation, physico-chemical, and biological characterization of several composite films containing graphene derivatives (graphene oxide or reduced graphene oxide) and curcumin as antioxidant in methylcellulose matrix. The morphostructural properties of the obtained composites were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The...
04. June 2016
Purpose The aim of our study was development of advanced third generation Curcumin self microemulsifying composition solid dispersion (Cur SMEC-SD) with high drug loading, improved stability, rapid in-vitro dissolution and enhanced bioavailability for improved therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Method The Cur SMEC-SD comprising polymers (KollidonVA64[KVA], Eudragits, HPMC and Soluplus) and self microemulsifying composition of surfactant:co-surfactant:oil were coated onto rapidly disintegrating...
01. April 2016
Hydrogels of a natural polysaccharide composed of Gum Arabic (GA) are appropriate materials for drug delivery, since they are water soluble, nontoxic and biocompatible. In this work, the effect of methacrylation on the properties of GA as pH-responsive hydrogel has been evaluated. Modified Gum Arabic (M-GAx), with different degrees of substitution, has been obtained by using different percentages of glycidyl methacrylate (x). It was observed that playing with the x value, gels with different...
11. January 2016
In the present study, we report the delivery of anti-cancer drug curcumin to cancer cells using mesoporous silica materials. A series of mesoporous silica material based drug delivery systems (S2, S4 and S6) were first designed and developed through the amine functionalization of KIT-6, MSU-2 and MCM-41 followed by the loading of curcumin. More
30. November 2015
The floating drug delivery system (FDDS) has become increasingly attractive system for gastroretentive dosage forms because it can prolong gastric retention time and improve drug bioavailability [1]. Using low density material of polypropylene foam powder is one of interestingapproach forFDDS development.This floating system has initial low density so it can float immediately without lag time. More
19. September 2015
Lipid-based formulations can be effective drug delivery systems for poorly water-soluble chemical entities, provided they are designed with careful selection of the excipients, based on their role in the delivery system and in relation to drug properties. The primary factor leading to increased bioavailability is the administration of the drug in a pre-dissolved state thereby avoiding the dissolution limiting step. More
16. July 2015
The influence of emulsifier type on the ability of excipient emulsions to improve the solubility, stability, and bioaccessibility of powdered curcumin was examined. Oil-in-water emulsions prepared using three different emulsifiers (whey protein isolate, caseinate, or Tween 80) were mixed with curcumin powder and then incubated at either 30 °C (to simulate applications of salad dressings) or 100 °C (to simulate applications of cooking sauces). More