- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
07. July 2018
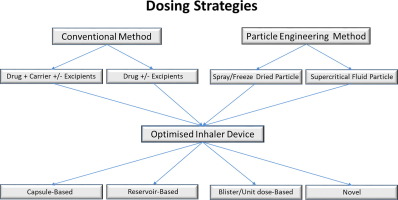
The pulmonary route of administration has been commonly used for local lung conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Recently, with the advent of new technologies available for both formulation and device design, molecules usually delivered at high doses, such as antibiotics and insulin to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) and diabetes, respectively, can now be delivered by inhalation as a dry powder. These molecules are generally delivered in milligrams instead of...
27. April 2018
This article reviews regulatory considerations for companies wishing to develop drugs for delivery via the respiratory tract (e.g., by oral inhalation or intranasally) using molecules previously approved for a different therapeutic indication and/or a different delivery route. Conceptually, such repurposing has many medical and business advantages, but turning promising ideas into real products requires overcoming a number of practical challenges. Obtaining regulatory approval to market a...
18. October 2017
In the drug delivery area, versatile therapeutic systems intended to yield customized combinations of drugs, drug doses and release kinetics have drawn increasing attention, especially because of the advantages that personalized pharmaceutical treatments would offer.
06. October 2017
In the field of nasal drug delivery, among the preparations defined by the European Pharmacopoeia, nasal powders facilitate the formulation of poorly water-soluble active compounds. They often display a simple composition in excipients (if any), allow for the administration of larger drug doses and enhance drug diffusion and absorption across the mucosa, improving bioavailability compared to nasal liquids. Despite the positive features, however, nasal products in this form still struggle to...
29. January 2017
Background Inhaled medication is the cornerstone of the pharmacological treatment for patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Several inhaler devices exist, and each device has specific characteristics to achieve the optimal inhalation of drugs. The correct use of inhaler devices is not granted and patients may incur in mistakes when using pressurized metered-dose inhalers (pMDIs) or dry-powder inhaler (DPIs). The incorrect use of inhaler devices can lead to a...
17. November 2016
Abstract Control of drug action through formulation is a vital and very challenging topic within pharmaceutical sciences. Cellulose nanofibers (CNF) are an excipient candidate in pharmaceutical formulations that could be used to easily optimize drug delivery rates. CNF has interesting physico-chemical properties that, when combined with surfactants, can be used to create very stable air bubbles and dry foams. Utilizing this inherent property, it is possible to modify the release kinetics of the...
17. February 2016
Dry powder formulations for nasal vaccine delivery offer versatile advantages compared to liquid formulations, such as increased storage stability and simplified administration. The objective of the present study was the development of a dry powder nasal vaccine formulation making use of antigen-loaded chitosan microparticles. Special emphasis was put on the development and characterization of a formulation which can realistically be used in humans by means of a nasal dry powder sprayer....
07. January 2016
Patient adherence is an important consideration when designing drug-delivery systems, devices, and related components and is leading advances in drug delivery. This patient-centric innovation is driving new ways to integrate pharmaceuticals, drug-delivery devices, wearables, and mobile technology as well as to develop greater patient-friendly drug-delivery devices that facilitate self-administration of drugs, including highly concentrated biologics. DCAT Value Chain Insights (VCI) examines the...