- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. September 2018
The current study was aimed to develop extended release (ER) pellets formulations containing zaltoprofen as a model drug and cross-linked starch-κ-carrageenan (Sκ-C) hydrogel composite as a binder and extended release polymer. The Sκ-C cross-linked hydrogel composites were prepared using a 32full factorial design approach and characterized by FTIR, DSC, XRD and SEM analysis. The matrix pellets were prepared by extrusion-spheronization technique and characterized production yield, FTIR, DSC,...
07. June 2018
3D printing evolved as a promising technique to improve individualization of drug therapy. In particular, when printing sustained release solid dosage forms, as for instance implants, inserts, and also tablets, estimation of the drug release profile in vivo is necessary. In most cases, corresponding analyses cannot be performed at hospital or community pharmacies. Therefore, the present study aimed to develop a sustained release drug delivery system produced via 3D printing, which allows dose...
28. September 2017
A comprehensive model with all effective phenomena in drug release such as diffusion, swelling and erosion was considered. In this work, a mathematical model was developed to describe drug release from controlled release HPMC matrices as a favorable system in pharmaceutical industries. As a novel study, the impact of the MCC presence as a filler in tablet preparation process was considered in the mathematical model. In addition, we found that the volume expansion of these polymeric matrices did...
15. October 2016
A previously presented physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model for immediate release (IR) methylphenidate (MPH) was extended to characterize the pharmacokinetic behaviors of oral extended release (ER) MPH formulations in adults for the first time. Information on the anatomy and physiology of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, together with the biopharmaceutical properties of MPH, was integrated into the original model, with model parameters representing hepatic metabolism and intestinal...
21. June 2016
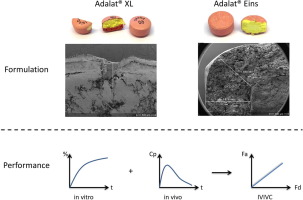
Aims Food intake is known to have various effects on gastrointestinal luminal conditions in terms of transit times, hydrodynamic forces and/or luminal fluid composition and can therefore affect the dissolution behavior of solid oral dosage forms. The aim of this study was to investigate and detect the dosage form-dependent food effect that has been observed for two extended-release formulations of nifedipine using in vitro dissolution tests. Methods Two monolithic extended release formulations,...
18. March 2016
The aim of this study was to develop, evaluate and compare extended release mini-matrices based on metoprolol tartrate (MPT) and either glyceryl behenate (GB) or glyceryl palmitostearate (GPS). Mini-matrices were produced by three different techniques: hot melt extrusion, compression of melt granulates and prilling. Hot-melt extrusion and compression of granules obtained from melted material proved to be reliable, robust and reproducible techniques with aim of obtaining extended release...
21. February 2016
The aim of this study focus on the extended release formulation on two aspects: the quantification and mechanistic research on pharmaceutical coating curing with a specific focus on how the moisture affect the curing; and in vivo and in vitro release of matrix ER tablets with implications on regulatory biowaiver using marketed products as practical examples. In all cases, it was found that the relative humidity of the environments were more important to reach higher extent of coalescence for EC...
18. January 2016
The objective was to formulate itopride HCl (ITP) extended release matrix-coated pellets by extrusion–spheronization and to investigate the influence of concentration and viscosity grade of different polymers on release of a highly water soluble drug. The matrix pellet formulations consisted of polymers (10–30%) like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC K4M, K15M, and K100M), ethyl cellulose (EC-7 cps), microcrystalline cellulose (10–30%) and a fixed quantity of lactose (10%). More
13. January 2016
Ethylcellulose is one of the most commonly used polymers to develop reservoir type extended release multiparticulate dosage forms. For multiparticulate extended release dosage forms, the drug release is typically governed by the properties of the barrier membrane coating. The ICH Pharmaceutical Development Guideline (ICH Q8) requires an understanding of the influence of critical material attributes and critical process parameters on the drug release of a pharmaceutical product. More
19. December 2015