- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
07. April 2018
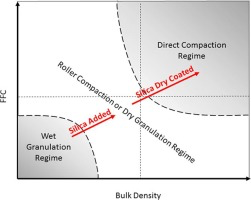
It has been shown that dry coating cohesive active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with nano-silica can improve packing and flow of their blends, facilitating high speed direct compressiontableting. This paper examines the broader scope and generality of previous work by examining three fine APIs; micronized Acetaminophen (mAPAP), coarse Acetaminophen (cAPAP) and micronized Ibuprofen(mIBU), and considers dry coating with both hydrophobic or hydrophilic nano-silica to examine the effect not...
16. September 2017
Abstract We aimed to understand the factors controlling mechanical particle coating using polymethacrylate. The relationship between coating performance and the characteristics of polymethacrylate powders was investigated. First, theophylline crystals were treated using a mechanical powder processor to obtain theophylline spheres (<100 μm). Second, five polymethacrylate latexes were powdered by spray freeze drying to produce colloidal agglomerates. Finally, mechanical particle coating was...
21. April 2017
Abstract The potential of fine excipient materials to improve the performance of carrier-based dry powder inhalation mixtures is well acknowledged. The mechanisms underlying this potential are, however, open to question till date. Elaborate understanding of these mechanisms is a requisite for rational rather than empirical development of ternary dry powder inhalation mixtures. While effects of fine excipient materials on drug adhesion to and detachment from surfaces of carrier particle have...
20. September 2016
Abstract Formation of core-shell nanocomposites of Fenofibrate and Itraconazole, model poorly water soluble drugs, via fluidized bed (FB) coating of their well-stabilized high drug loaded nanosuspensions is investigated. Specifically, the extent of dissolution enhancement, when fine carrier particles (sub–50 μm) as opposed to the traditional large carrier particles (>300 μm) are used, is examined. This allows testing the hypothesis that greatly increased carrier surface area and more...
25. May 2016
Abstract: The nasal route receives a great deal of attention as a non-invasive method for the systemic administration of drugs. For nasal delivery, specific formulations containing excipients are used. Because of the sensitive respiratory mucosa, not only the active ingredients, but also additives need to be tested in appropriate models for toxicity. The aim of the study was to measure the cytotoxicity of six pharmaceutical excipients, which could help to reach larger residence time, better...
25. May 2016
14. March 2016
This work investigates the dispersion performance of fine lactose particles as function of processing time, and compares it to the API, using Beclomethasone Dipropionate (BDP) as model API. The total load of fine particles is kept constant in the formulations while the proportions of API and lactose fines are varied. Fine particle assessment demonstrates that the lactose fines have higher dispersibility than the API. For standard formulations, processing time has a limited effect on the Fine...
13. March 2016
l-Leucine (LL) has been widely used to enhance the dispersion performance of powders for inhalation. LL can also protect powders against moisture, but this effect is much less studied. The aim of this study was to investigate whether LL could prevent moisture-induced deterioration in in vitro aerosolization performances of highly hygroscopic spray-dried powders. Disodium cromoglycate (DSCG) was chosen as a model drug and different amounts of LL (2–40% w/w) were added to the formulation, with...
03. August 2015
This study investigates the effects of a variety of coating materials on the flowability and dissolution of dry-coated cohesive ibuprofen powders, with the ultimate aim to use these in oral dosage forms. A mechanofusion approach was employed to apply a 1% (w/w) dry coating onto ibuprofen powder with coating materials including magnesium stearate (MgSt), l-leucine, sodium stearyl fumarate (SSF) and silica-R972. More
10. July 2015
This study aims to investigate the effect of carrier characteristics and dosator capsule filling operation on the in vitro deposition of mixtures containing salbutamol sulphate (SS) and lactose and mannitol as model carrier materials. The carrier surfaces of lactose and mannitol were modified via wet decantation. More