- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. September 2018
Diabetes mellitus is a highly prevalent metabolic and chronic disease affecting millions of people in the world. The most common route of insulintherapy is the subcutaneous injection due to its low bioavailability and enzymatic degradation. The search for effective and high patient compliance insulin delivery systems has been a major challenge over many decades. The polysaccharide-based nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for insulin oral administration have recently attracted substantial...
31. August 2018
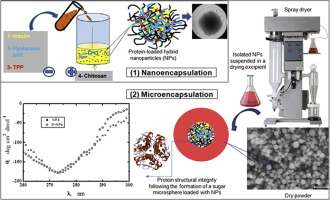
Combined micro- and nanosystems are appealing for pulmonary protein delivery, fulfilling the specific physiological requirements for efficient outcomes in-vivo. However, fabrication of protein formulations may impose stresses perturbing protein conformational stability and, hence, biological activity. Herein, a protein, insulin (INS), was nanoencapsulated inside chitosan nanoparticles (CS NPs) by ionic gelation. By spray drying, the resultant protein-loaded NPs were further encapsulated with a...
11. January 2018
Nanoparticles or microparticles created by physical complexation between two polyelectrolytes may have a prospective use as an excipient for oral insulin administration. Natural polymers such as tragacanth, alginate, dextran, pullulan, hyaluronic acid, gelatin and chitosan can be potential candidates for this purpose. In this research, insulin particles were prepared by the inclusion of insulin into a tragacanth hydrogel.
07. January 2018
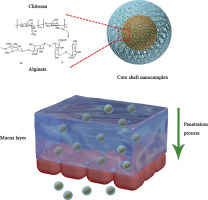
The objective of this study was to design intestinal mucus-penetrating core-shell nanocomplex by functionally mimicking the surface of virus, which can be used as the carrier for peroral delivery of macromolecules, and further understand the influence of nanocomplex surface properties on the mucosal permeation capacity.
28. September 2017
Purpose of Review Faster aspart is a new formulation of insulin aspart (IAsp) produced by adding the excipients niacinamide and L-arginine. As this new, “ultra-rapid insulin” is available in the EU-market and Canada, the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics data is summarized. Recent Findings Faster aspart shows an earlier onset of appearance of insulin in the bloodstream after subcutaneous administration and an earlier onset of glucose-lowering action and a higher glycemic effect within...
11. September 2017
Nanoparticles have demonstrated significant advancements in potential oral delivery of insulin. In this publication, we review the current status of polymeric, inorganic and solid-lipid nanoparticles designed for oral administration of insulin.
14. August 2017
Insulin, a hormonal drug for the management of diabetes mellitus has continued to attract attention of many researchers and pharmaceutical formulators for more than a decade. However, its low oral bioavailability due to the activities of intestinal enzymes restricts its route of administration to only the parenteral route.
28. June 2017
Sustained release systems for therapeutic proteins have been widely studied targeting to improve the action of these drugs. Molecular entrapping of proteins is particularly challenging due to their conformational instability.
08. March 2017
Abstract Associative interactions between folic acid and proteins are well known. This work leverages these interactions to engineer folic acid nanoparticles for controlled release of insulin during diabetes therapy. The insulin-loaded folic acid nanoformulation is synthesized during this study and more than 70% protein loading with less than 10% insulin loss have been maintained during the synthesis process. The folic acid nanoparticles of 50–150 nm size are further characterized in the...
27. February 2017
Abstract We have reported that cell-penetrating peptides, such as oligoarginine, act as powerful absorption enhancers for the development of oral insulin delivery systems. However, the minimal essential sequence of oligoarginine that stimulates intestinal insulin absorption remains unclear. Therefore, the present study was conducted to clarify this minimum sequence of oligoarginine and to examine the effect of single cationic amino acid arginine on the intestinal and oral absorption of insulin....