- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
31. July 2018
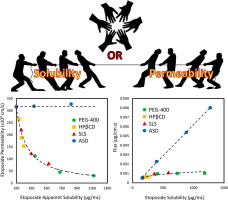
Poor aqueous solubility is a major challenge in today's biopharmaceutics. While solubility-enabling formulations can significantly increase the apparent solubility of the drug, the concomitant effect on the drug's apparent permeability has been largely overlooked. The mathematical equation to describe the membrane permeability of a drug comprises the membrane/aqueous partition coefficient, which in turn is dependent on the drug's apparent solubility in the GI milieu, suggesting that the...
01. October 2017
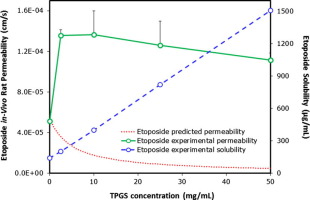
Vitamin E TPGS (TPGS) has both surfactant and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitory effects. While surfactants were previously found to cause solubility-permeability tradeoff, TPGS P-gp inhibitory effects may change this unfavorable interplay. The purpose of this research was to investigate the solubility-permeability interplay when using TPGS vs. amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) as oral drug delivery systems for the anticancer, P-gp substrate, lipophilic drug etoposide. The concentration-dependent...
02. March 2017
Zidovudine (AZT) mucoadhesive solid dispersions (SD) were prepared using a sodium starch glycolate (SSG) and hypromellose phthalate (HPMCP) mixtures as carrier to enhance the intestinal permeability and bioavailability of zidovudine. SDs were prepared using the co-precipitation method followed by solvent evaporation and characterized according to their physicochemical properties such as particle size, crystallinity, thermal behavior, and liquid uptake ability. In vitro drug dissolution,...
27. February 2017
Abstract We have reported that cell-penetrating peptides, such as oligoarginine, act as powerful absorption enhancers for the development of oral insulin delivery systems. However, the minimal essential sequence of oligoarginine that stimulates intestinal insulin absorption remains unclear. Therefore, the present study was conducted to clarify this minimum sequence of oligoarginine and to examine the effect of single cationic amino acid arginine on the intestinal and oral absorption of insulin....
13. February 2017
Abstract In order to save time and resources in early drug development, in vitro methods that correctly predict the formulation effect on oral drug absorption are necessary. The aim of this study was to 1) evaluate various BCS class II drug formulations with in vitro methods and in vivo in order to 2) determine which in vitro method best correlates with the in vivo results. Clarithromycin served as model compound in formulations with different particle sizes and content of excipients. The...
04. January 2017
Abstract This research addresses the development and in vitro evaluation of a microparticulate system intended for intestine-targeted delivery of curcumin (CRM), a natural polyphenol with anti-inflammatory properties. Microspheres (Ms) based on zein (ZN) and Gantrez® AN119 (PVMMA) were prepared by spray-drying and coated with a pH-sensitive polymer (Eudragit® FS30D). An experimental design was performed to optimize the microparticulate formulation. A detailed characterization of systems was...
15. December 2016
Abstract Predictive in vitro test methods addressing the parameters relevant to drug release in the pediatric gastrointestinal tract could be an appropriate means for reducing the number of in vivo studies in children. However, dissolution models addressing the particular features of pediatric gastrointestinal physiology and typical pediatric dosing scenarios have not yet been described. The objective of the present study was to combine the knowledge on common vehicle types and properties and...
11. October 2016
Abstract In this present study, the secretory transport of P-gp substrates, rhodamine 123 and digoxin, was evaluated using a Caco-2/HT29-MTX co-culture characterized by an efflux mechanism and a paracellular permeability closer to the human intestinal barrier compared to the Caco-2 monolayer gold standard. The influence of simulated intestinal fluids termed FeSSIF and FaSSIF on the intestinal absorption was also assessed in comparison with a conventional saline buffer. Labrasol® ALF and...
28. September 2016
Abstract Lipid nanoparticles and their multiple designs have been considered appealing nanocarrier systems. Bringing the benefits of these nanosystems together with conventional coating technology clearly results in product differentiation.This work aimed at developing an innovative solid dosage form for oral administration based on tableting nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), coated with conventional polymer agents. NLC dispersions co-encapsulating olanzapine and simvastatin (Combo-NLC) were...
24. June 2016
Abstract The aim of this study was the development of zeta potential changing self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS). Various cationic surfactants were incorporated into a formulation consisting of 30% Cremophor EL, 30% Capmul MCM, 30% Captex 355 and 10% propylene glycol (w/w). A substrate of intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP), 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidic acid sodium (PA), was thereafter incorporated into SEDDS. Size, zeta potential and polydispersity index were...