- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
05. March 2018
This study presents a framework for process and product development on a continuous direct compression manufacturing platform. A challenging sustained release formulation with high content of a poorly flowing low density drug was selected. Two HPMC grades were evaluated as matrix former: standard Methocel CR and directly compressible Methocel DC2. The feeding behavior of each formulation component was investigated by deriving feed factor profiles.
01. March 2018
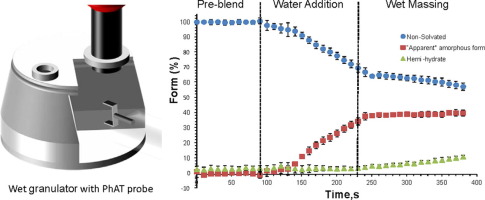
Form changes during drug product processing can be a risk to the final product quality in terms of chemical stability and bioavailability. In this study, online Raman spectroscopy was used to monitor the form changes in real time during high shear wet granulation of Compound A, a highly soluble drug present at a high drug load in an extended release formulation. The effect of water content, temperature, wet massing time and drying technique on the degree of drug transformation were examined.
22. March 2017
Abstract: Background: Conventional dosage forms of neomycin sulphate suffer from different drawbacks like spillage, poor penetration, low bioavailability, etc. In situ ophthalmic gel can overcome these problems by improving bioavailability, decreasing spillage and diminish the need for recurrent application. Thus, the aim of the present work was to prepare and evaluate in situ ophthalmic gel of neomycin sulphate for sustained ocular delivery. Method: Two polymers, sodium alginate (0.2-0.7%) and...
09. August 2016
Abstract Direct delivery of sustained therapeutic levels of mesalamine (MS) via rectal systems to manage distal forms of ulcerative colitis was studied. The High molecular weight hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC K4M) polymer was combined with hydrophilic surfactants to control polymer hydration process allowing optimization of the mucoadhesive and controlled drug release properties for the rectal systems. Physical mixtures and granules of MS and HPMC K4M were prepared and in vitro...
28. July 2016
ABSTRACT Background: Gastroretentive floating microsphere containing Lafutidine, a second generation histamine H2–receptor antagonist were prepared by ionotropic gelation technique by using sodium alginate, HPMC K4M, ethyl cellulose as polymers, sodium bicarbonate as gas generating agent and calcium chloride as cross linking agent. Objective: To formulate a system to remain in the stomach for prolonged and predictable period in order to enhance the drug bioavailability. Method: They were...
08. March 2016
Introduction: Oral sustained release gastro retentive dosage forms offer several advantages for drugs having absorption from the upper gastrointestinal tract to improve the bioavailability of medications which have narrow absorption window. The aim of the study was to develop a floating bioadhesive drug delivery system exhibiting a unique combination of floatation and bioadhesion to prolong the residence in the stomach using atenolol as a model drug. Methods: Prior to compression, polymeric...
08. November 2015
Polysaccharides are suitable for application as hydrophilic matrices because of their ability to hydrate and swell upon contact with fluids, forming a gel layer which controls drug release. When extracted from plants, polysaccharides often contain significant quantities of starch that impacts upon their functional properties. This study aimed to evaluate differences in swelling, erosion and drug release from matrix tablets prepared from grewia gum (GG) and starch-free grewia gum (GDS) extracted...