- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
06. February 2017
Abstract Liquid adsorption on solid adsorbent carriers is an emerging technique for oral lipid-based drug delivery systems. The purpose of the current study is to convert liquid into solid self-emulsifying lipid formulations (SELFs) using an inorganic adsorbent Neusilin® grade US2 (NUS2) and investigate in vitro dissolution and digestion performance of the model antipsychotic compound risperidone. Methods The liquid SELFs were designed using various oils, nonionic surfactants and converted...
22. November 2016
Abstract Gastrointestinal drug administration is the preferred route for the majority of drugs however, the natural physiology and physicochemistry of the gastrointestinal tract is critical to absorption but complex and influenced by factors such as diet or disease. The pharmaceutical sciences drive for product consistency has led to the development of in vitro product performance tests whose utility and interpretation is hindered by the complexity, variability and a lack of understanding. This...
05. November 2016
Biopharmaceutics have been recognized as the drugs of choice for the treatment of several diseases, mainly due to their high selectivity and potent action. Nonetheless, their oral administration is a rather challenging problem, since their bioavailability is significantly hindered by various physiological barriers along the GI tract, including their acid-induced hydrolysis in the stomach, their enzymatic degradation throughout the GI tract and their poor mucosa permeability. Lipid-based...
13. August 2016
Abstract The majority of newly discovered oral drugs are poorly water soluble, and co-administration with lipids has proven effective in significantly enhancing bioavailability of some compounds with low aqueous solubility. Yet, lipid-based delivery technologies have not been widely employed in commercial oral products. Lipids can impact drug transport and fate in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through multiple mechanisms including enhancement of solubility and dissolution kinetics,...
09. August 2016
Abstract Many studies had been focused on designing tacrolimus sustained release preparations based on solid dispersion technique, but no one had tried to employ mesoporous silica as the carrier material to realize this goal. The purpose of this study was to develop a novel, simple and environmental friendly drug loading method with mesoporous silica to obtain tacrolimus sustained-release preparation. Tacrolimus was firstly dissolved in the molten mixed lipid composed of Compritol 888 ATO and...
02. June 2016
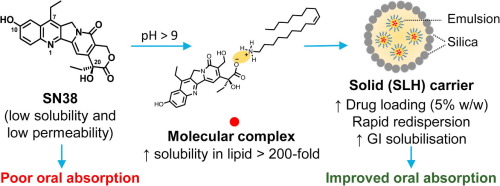
SN38 (7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin) is a highly potent anti-cancer compound. However, it is poorly soluble in pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, thus the direct formulation and delivery is restricted. The current study focused on lipid-based formulation design to enable oral delivery of SN38 at high doses and at therapeutic levels. The pH dependent ionisation property of SN38 was utilized to form a molecular complex with the cationic surfactant, oleylamine and this increased (>...
16. November 2015
Identification of the usefulness of lipid-based formulations (LBFs) for delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs is at date mainly experimentally based. In this work we used a diverse drug dataset, and more than 2,000 solubility measurements to develop experimental and computational tools to predict the loading capacity of LBFs. More
02. November 2015
Objective: To investigate the viscosity-temperature relationship of lipid-based materials (fatty alcohol, fatty acid, fatty ester and glycerides) amenable for spray congealing. More
21. October 2015
Nowadays exploration of novel lipid-based formulations is akin to a magnet for researchers worldwide for improving the in vivo performance of highly lipophilic drugs. Over the last few years, new compositions of lipids have been developed, and the probable bioavailability enhancement has been investigated. We reviewed the most recent data dealing with backlogs of conventional lipid-based formulations such as physical instability, limited drug loading capacities, drug expulsion during storage...
05. October 2015