- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
27. July 2018
The present study elucidated the advantages of using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose E5 (HPMC) as auxiliary excipient in maintaining storage stability and solubilization ability for curcumin amorphous solid dispersion (Cur ASDs) formulated by Eudragit E100 (E100). Polarized light microscopy and in vitro dissolution experiment was applied for confirming the ability of HPMC on inhibiting crystallization thereby maintaining storage stability in Cur ASDs. Meanwhile, as a non-ionic surfactant, HPMC...
10. October 2017
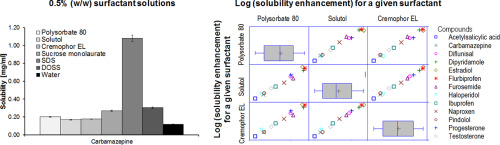
Solubility screening in different surfactant solutions is an important part of pharmaceutical profiling. A particular interest is in low surfactant concentrations that mimic the dilution of an oral dosage form.
03. March 2017
Abstract Fenofibrate, a drug of fibrate class, is mainly used to reduce cholesterol levels in patients at risk of cardiovascular disease. However, bioavailability of fenofibrate is often low and unpredictably due to its poor solubility. Microparticle entrapped micelles (MEM) technology is a novel method of incorporating surfactants in solid dosage form for improving in vitro and in vivo performance of poorly water soluble drugs. Increasing the fenofibrate solubility by MEM technology has not...
10. November 2016
Abstract Many of the newly developed drugs for cancer, and some of those for cardiovascular disease, are poorly soluble in water and cannot be taken orally. This can be overcome by employing a new and effective delivery system utilizing nanotechnology. We present a new method for oral preparation of poorly soluble drugs that entails assembling (printing) drug-loaded polymeric micelles into sub-100 nm orally acceptable nanorods (NRs). Due to their small size, these NRs will have a high...
13. August 2016
Abstract The majority of newly discovered oral drugs are poorly water soluble, and co-administration with lipids has proven effective in significantly enhancing bioavailability of some compounds with low aqueous solubility. Yet, lipid-based delivery technologies have not been widely employed in commercial oral products. Lipids can impact drug transport and fate in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through multiple mechanisms including enhancement of solubility and dissolution kinetics,...