- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
15. April 2018
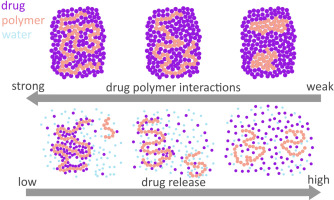
The maximum achievable concentration of a drug in solution is dictated by the chemical potential of the solid form. Because an amorphous solid has a higher chemical potential than the corresponding crystal form, in the absence of phase transformations, a higher transient solubility is expected. However, the chemical potential of an amorphous drug can be reduced by mixing with another component. Therefore, upon mixing with a polymer to form an amorphous solid dispersion (ASD), the maximum...
08. January 2018
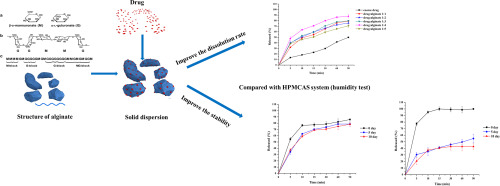
The objective of this study was to explore the feasibility of using alginate as a promising diphase solid dispersion carrier to enhance dissolution rate of BCS II drugs with improved stability. Taking lovastatin and indomethacin as model drugs, solvent evaporation method was used to prepare solid dispersions.
24. March 2017
ABSTRACT Introduction: For almost two decades there has been intense debate about whether the amorphous solid state form could resolve the solubility problems and subsequent bioavailability issues of many small molecule drugs. Since the amorphous form is a high energy and unstable state of solid matter, any material in that form requires stabilization. Areas covered: This review examines the technologies being exploited to stabilize the amorphous state in co-amorphous formulations. The review...
10. January 2017
Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the drug-polymer miscibility of GENE-A, a Genentech molecule, and Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-acetate succinate (HPMC-AS), a polymer, using computational and experimental approaches. The Flory-Huggins interaction parameter,χ, was obtained by calculating the solubility parameters for GENE-A and HPMC-AS over the temperature range of 25–100 °C to obtain the free energy of mixing at different drug loadings (0-100%) using the Materials Studio...
22. August 2016
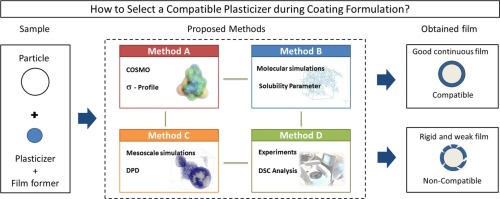
Abstract During the formulation of solid dosage forms coating, plasticizers are added to the film forming polymer to improve the mechanical properties of the coating shell of the drug product. For the coating formulation to be successful and in order to produce flexible continuous film, the plasticizer should be compatible with the film forming polymer (i.e. high plasticizer-polymer miscibility in solid dispersion) (McGinity and Felton, 2008). This paper proposes and compares different...
12. June 2016
Introduction: For almost two decades there has been intense debate about whether the amorphous solid state form could resolve the solubility problems and subsequent bioavailability issues of many small molecule drugs. Since the amorphous form is a high energy and unstable state of solid matter, any material in that form requires stabilization. Areas covered: This review examines the technologies being exploited to stabilize the amorphous state in co-amorphous formulations. The review emphasizes...
15. September 2015
Hot-melt extrusion technology has been widely reported for producing amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble compounds. A number of studies revealed that enteric polymers containing ionizable groups are able to improve the physical stability and maintain drug supersaturation, thereby enhancing oral bioavailability. More
06. September 2015
Objective of this work was to understand the mechanism of formation of celecoxib nanocrystals in celecoxib: mannitol nanocrystalline solid dispersion (NSD). Solution of celecoxib and mannitol was spray dried in 1:1 (g:g) proportion to obtain NSD, with average crystallite size of 214.07 ± 45.27 nm. Solubility parameters of celecoxib and mannitol were 23.1 MPa1/2 and 38.5 MPa1/2, respectively, hinting their immiscibility. More