- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. September 2018
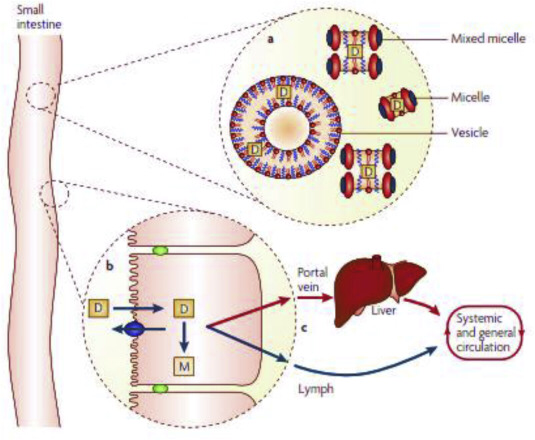
Diabetes mellitus is a highly prevalent metabolic and chronic disease affecting millions of people in the world. The most common route of insulintherapy is the subcutaneous injection due to its low bioavailability and enzymatic degradation. The search for effective and high patient compliance insulin delivery systems has been a major challenge over many decades. The polysaccharide-based nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for insulin oral administration have recently attracted substantial...
31. August 2018
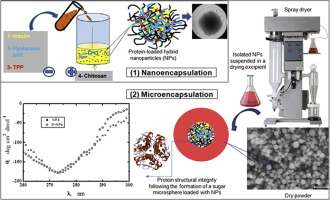
Combined micro- and nanosystems are appealing for pulmonary protein delivery, fulfilling the specific physiological requirements for efficient outcomes in-vivo. However, fabrication of protein formulations may impose stresses perturbing protein conformational stability and, hence, biological activity. Herein, a protein, insulin (INS), was nanoencapsulated inside chitosan nanoparticles (CS NPs) by ionic gelation. By spray drying, the resultant protein-loaded NPs were further encapsulated with a...
30. August 2018
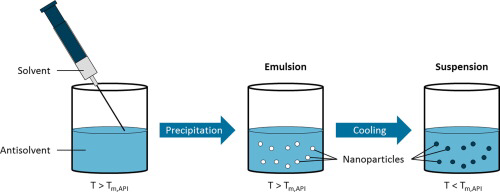
Antisolvent precipitation of poorly water-soluble drugs is a promising formulation technique to synthesize amorphous nanoparticles. The dissolution behavior of these nanoparticles is improved because of the high specific surface area and the amorphous state, leading to an enhanced bioavailability of the drug molecules. Nevertheless, stabilization of precipitated drug nanoparticles against agglomeration and recrystallization, which constitutes a key issue for further processing steps, has turned...
24. August 2018
In today's drug development world, combinatorial chemistry, high-throughputscreening, and genomics have provided a technologic platform that produces a large number of new chemical entities withtherapeutic potential each year. Its outcome the new chemical entities shifted towards higher molecular weight and increasing lipophilicity that results in poor water solubility which primarily affectsthe bioavailability of orally administered drugs. Hence, the poor aqueoussolubility not only limits the...
15. May 2018
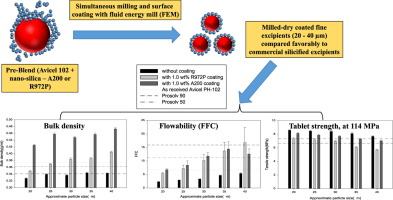
Asolventless process for simultaneously milling and dry coating microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) was investigated for producing fine excipients in five different sizes (∼20, 25, 30, 35, 40µm) havinghigh bulk density (BD), good flow function coefficient (FFC), and excellent compaction. Avicel PH-102, used as the starting material, was milled and coated with two grades of silicas, hydrophobic andhydrophilic (R972P and A200), using a fluid energy mill (FEM). Through judicious selection of the...
07. May 2018
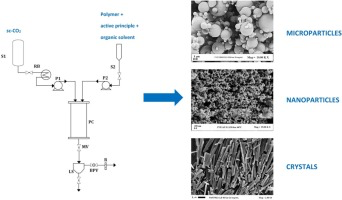
Supercritical antisolvent precipitation (SAS) has been successfully used to produce microparticles and nanoparticles of controlled size and distribution either as a single precipitates or by coprecipitation of two or more compounds. SAS coprecipitation process has produced different particles morphologies and, differently from the single compound SAS precipitation, process mechanisms involved have never been elucidated and the effectiveness of the technique has been verified only in some cases....
20. April 2018
Silica-based nanoparticles are used as excipients in pharmaceutical technology. Recently, mesoporous silica nanoparticles have emerged as drug delivery systems. Their porous structure enables the high drug-loading of drugs with poor water solubility. The silica matrix protects entrapped drugs against enzymatic degradation. Furthermore, the premature release of drugs is hindered by pore-gating strategies. Adding a targeting ligand to the silica-based nanoparticles directs them to diseased cells...
01. March 2018
Most of antibacterial and antiviral agents and drugs for the treatment of central nervous system and cancer are water-insoluble, which reduces their bioavailability. The bioavailability of substances can be increased by using a dosage form such as nanosuspension.
02. February 2018
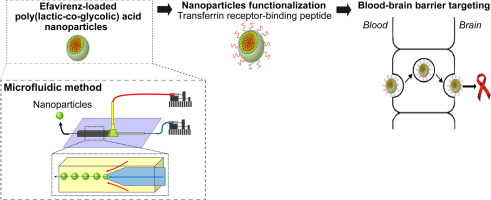
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) uses the brain as reservoir, which turns it as a promising target to fight this pathology. Nanoparticles (NPs) of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) are potential carriers of anti-HIV drugs to the brain, since most of these antiretrovirals, as efavirenz (EFV), cannot surpass the blood–brain barrier (BBB).
26. January 2018
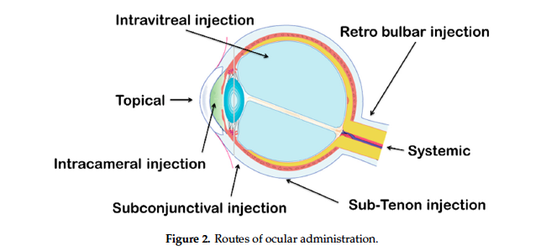
The last fifty years, ophthalmic drug delivery research has made much progress,
challenging scientists about the advantages and limitations of this drug delivery approach. Topical eye
drops are the most commonly used formulation in ocular drug delivery. Despite the good tolerance
for patients, this topical administration is only focus on the anterior ocular diseases and had a high
precorneal loss of drugs due to the tears production and ocular barriers. Antibiotics are popularly
used in solution