- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
27. April 2018
Although bioavailability of peptides administered through nasal route is still under 1% because of low membrane permeability, a short local residence time and a high metabolic turnover in the nasal epithelium but the richly supplied vascular nature of the nasal mucosa coupled with its high drug permeation makes the nasal route of administration attractive for many drugs including proteins and peptides. Thiolated polymers (thiomers) which are also recognized as mucoadhesive polymers, discovered...
28. February 2018
This study aimed to formulate a solid dosage form as decongestant for intranasal application. Nine formulations (A-K) based on gelatin and other polymers were manufactured following the solvent evaporation method. Fabricated patches were characterized according to uniformity of weight, thickness, transparency and surface pH, tensile strength and elongation at break. Adhesiveness was assessed by tack test and bioadhesive assay on the nasal porcine mucosa. Naphazoline was incorporated in the diffe
16. January 2018
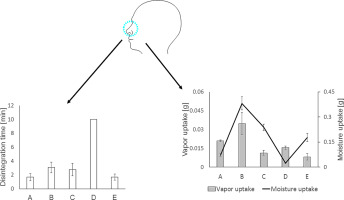
This present study intended to provide nasal adhesive formulations for the topical treatment of dry nasal syndrome. Mucoadhesive films were prepared according to solvent evaporation method consisting of well-known polymers such as gellan and carboxymethyl cellulose. Mucoadhesive films (A–E) were evaluated in respect to their physicochemical properties, stability, disintegration behavior and tensile strength.
11. January 2018
The purpose of present research work was to develop mucoadhesive microparticles of Zaleplon for nasal delivery with the aim to avoid hepatic first-pass metabolism, improve therapeutic efficacy and enhance residence time in the treatment of insomnia.
06. October 2017
In the field of nasal drug delivery, among the preparations defined by the European Pharmacopoeia, nasal powders facilitate the formulation of poorly water-soluble active compounds. They often display a simple composition in excipients (if any), allow for the administration of larger drug doses and enhance drug diffusion and absorption across the mucosa, improving bioavailability compared to nasal liquids. Despite the positive features, however, nasal products in this form still struggle to...
22. July 2017
Zolmitriptan (ZT) is a well-tolerated drug in migraine treatment suffering from low bioavailability due to low amount of the drug that reaches the brain after oral and nasal delivery.
24. March 2017
Abstract In situ gel drug delivery systems are in solution form before administration but once administered, undergo gelation in situ, to form a gel. In the present study nasal in situ gel of Phenylephrine hydrochloride was prepared for the treatment of nasal infections to provide sustained release of drug and to attain site specific action. Carbopol 934 was used as a pH triggered polymer and Poloxamer 188 was used as thermo sensitive agent. Different formulations were prepared by varying the...
27. October 2016
Abstract Mucoadhesive in situ gelling systems (soluble gels) have received considerable attention recently as effective stimuli-transforming vectors for a range of drug delivery applications. Considering this fact, the present work involves systematic formulation development, optimization, functional evaluation and ex vivo performance of thermosensitive soluble gels containing dexamethasone 21-phosphate disodium salt (DXN) as the model therapeutic. A series of in situ gel-forming systems...
17. October 2016
28th October 2016 in Basel, Switzerland presented by Claudia Mattern, Dr. rer. nat., Adj. Prof. Leiterin M et P Pharma AG Emmetten Video Registration
30. September 2016
Abstract Despite the numerous advantages of powder formulations, few studies have described their nasal drug absorption. The first aim of this study was to compare the drug absorption from powder formulation with that from a liquid formulation in rats. Since pharmaceutical excipients are usually added to most powder formulations, the second aim of the study was to investigate the effect of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) on nasal drug absorption from the powder. Three types of HPC with different...