- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. July 2018
Thixotropic gels, thermosoftened systems, and self-emulsifying systems have expanded the range of potential excipients. Liquid-filled hard capsules (LFHCs) are typically composed of a shell of gelatin or hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and filled with compatible liquids or compositions that can flow below 70 oC. LFHC technology offers several advantages over other solid dosage forms (1). It is crucial, however, to select excipients that are compatible with capsule shell integrity and...
05. May 2018
Along with the development of novel drug delivery systems the material science is also advancing. Conventional and novel synthetic or natural excipients provide opportunities to design dosage forms of the required features including their bioavailability.
16. March 2018
Pharmaceutical drug products contain various excipients in combination with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), and those excipients have the potential to have as impurities reactive oxygen species that can react directly with the API and lead to oxidative degradation. Such degradation can impact long-term stability of the drug product, reduce drug product purity, limit shelf life, and increase time to market.
15. February 2018
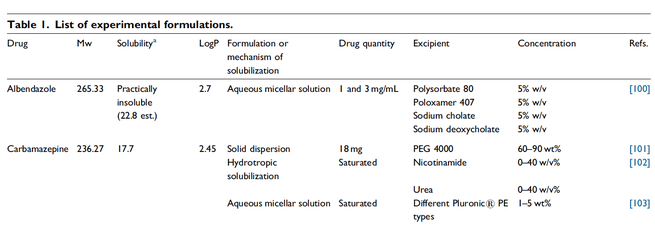
The poor oral bioavailability of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) resulting from low solubility is one of the important challenges in pharmaceutical technology. Over the last two decades the number of relatively insoluble drugs has grown steadily. Nowadays it is estimated that approximately 70% of new drug candidates are characterized by poor solubility.
14. February 2018
Solid oral dosage forms (SODF) are drug vehicles commonly prescribed by physicists in primary and secondary cares, as they are the most convenient for the patient and facilitate therapy management. Concerns regarding unintended adhesion of SODF during oro-esophageal transit remain, especially in multimorbid patients, bedridden patients and patients suffering from dysphagia.
23. January 2018
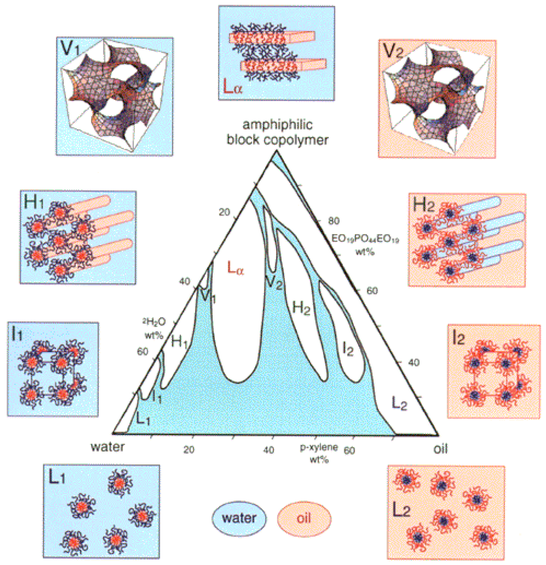
Poloxamers, also known as Pluronics®, are block copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and poly(propylene oxide) (PPO), which have an amphiphilic character and useful association and adsorption properties emanating from this. Poloxamers find use in many applications that require solubilization or stabilization of compounds and also have notable physiological properties, including low toxicity. Accordingly, poloxamers serve well as excipients for pharmaceuticals.
23. January 2018
Glucagon is a peptide hormone used for the treatment of hypoglycemia; however, its clinical potential is limited by its insolubility and instability in solution. Herein, the encapsulation, stabilization, and release of glucagon by trehalose glycopolymer nanogels are reported. Methacrylate-functionalized trehalose is copolymerized with pyridyl disulfide ethyl methacrylate using free radical polymerization conditions to form trehalose glycopolymers with thiol-reactive handles.
11. January 2018
The oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can be improved by the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) where the API is dissolved in polymeric excipients. Desired properties of such ASDs like storage stability, dissolution behavior, and processability can be optimized by additional excipients. In this work, the influence of so-called low-molecular-weight excipients (LMWEs) on the phase behavior of ASDs was investigated.
10. January 2018
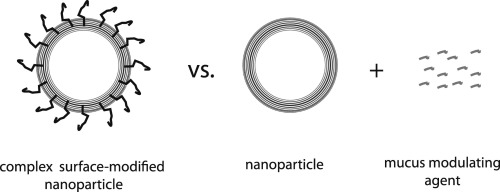
Nanoparticulate drug delivery systems (nDDS) offer a variety of options when it comes to routes of administration. One possible path is crossing mucosal barriers, such as in the airways and in the GI tract, for systemic distribution or local treatment. The main challenge with this administration route is that the size and surface properties of the nanoparticles, as opposed to small molecular drugs, very often results in mucosal capture, immobilization and removal, which in turn results in a ..
13. December 2017
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a chemically inert, amphiphilic polymer used as an excipient in many pharmaceuticals for decades, and as a conjugate with biologicals (ie, PEGylation) since 1990. To date, the US FDA has approved 14 PEGylated therapies with diverse indications.