- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
11. September 2018
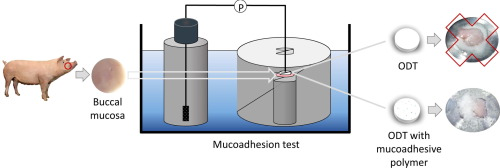
Oromucosal drug delivery is necessary when a local effect in the oral cavity is required. Bioadhesive formulations should be advantageous because a larger fraction of the active principal is retained at the site of action allowing for an enhanced and prolonged effect. Despite a variety of mucoadhesion test systems being described in literature, none of these in-vitro tests does relate to physiological conditions in the oral cavity and suites for the testing of complete dosage forms, e.g....
30. May 2018
Blindness and vision impairment are the most devastating global health problems resulting in a substantial economic and social burden. Delivery of drug to particular parts of the anterior or posterior segment has been a major challenge due to various protective barriers and elimination mechanisms associated with the unique anatomical and physiological nature of the ocular system. Drug administration to the eye by conventional delivery systems results in poor ocular bioavailability (< 5%)....
03. April 2017
Abstract Hyaluronic acid (HA) solutions effectively lubricate the ocular surface and are used for the relief of dry eye related symptoms. However, HA undergoes rapid clearance due to limited adhesion, which necessitates frequent instillation. Conversely, highly viscous artificial tear formulations with HA blur vision and interfere with blinking. Here, we developed an HA-eye drop formulation that selectively binds and retains HA for extended periods of time on the ocular surface. We synthesized...
17. November 2016
Abstract Control of drug action through formulation is a vital and very challenging topic within pharmaceutical sciences. Cellulose nanofibers (CNF) are an excipient candidate in pharmaceutical formulations that could be used to easily optimize drug delivery rates. CNF has interesting physico-chemical properties that, when combined with surfactants, can be used to create very stable air bubbles and dry foams. Utilizing this inherent property, it is possible to modify the release kinetics of the...
19. September 2015