- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. October 2018
The production of 3D-printed drugs holds promise for future personalized medicine. Here, we prepared tablets containing naftopidil as a model drug using a semi-solid extrusion-type 3D bioprinter applicable for tissue engineering. A hydrogel is typically used as the printer ink for 3D bioprinters, and we incorporated various amounts of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel (30%, 40% and 50% gel) into the printer ink. The resulting 3D-printed gel product was dried to obtain tablets. The...
06. September 2018
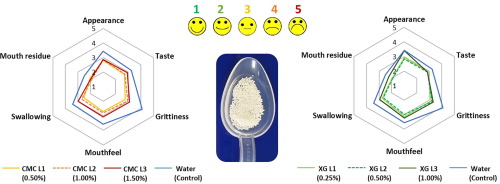
Multiparticulate formulations based on pellets, granules or beads, could be advantageous for paediatrics, geriatrics and patients with swallowing difficulties. However, these formulations may require suitable administration media to facilitate administration. The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of administration media properties on palatability and ease of swallowing of multiparticulates. A range of vehicles were developed using xanthan gum (XG) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)...
09. March 2018
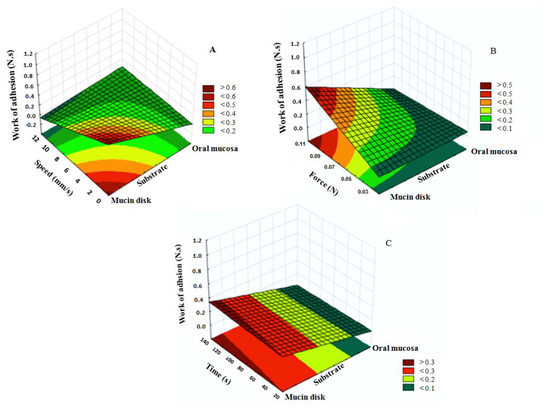
The process of mucoadhesion has been widely studied using a wide variety of methods, which are influenced by instrumental variables and experiment design, making the comparison between the results of different studies difficult. The aim of this work was to standardize the conditions of the detachment test and the rheological methods of mucoadhesion assessment for semisolids, and introduce a texture profile analysis (TPA) method.
29. August 2017
Electrospinning of Eudragit® FS 100 was investigated for the first time.
• Novel AC electrospinning produced excellent quality nano fibers at high throughput.
• Melt rheology of Eudragit® FS 100 was thoroughly explored.
• Eudragit® FS-based solid dispersions provided excellent control on release of poorly soluble spironolactone as pH varied.
24. August 2017
The flowing properties of 10 lactose powders commonly used in pharmaceutical industries have been analyzed with three recently improved measurement methods. The first method is based on the heap shape measurement.
03. April 2017
Abstract The focus was on the development of medicated foam for incorporation of two incompatible active agents for psoriasis treatment; i.e., lipophilic cholecalciferol, and hydrophilic salicylic acid. Emphasis was given to formulation of a propellant-free foam, with sufficient foaming properties, physical and chemical stability, and low irritancy potential to maintain relevance for later translation into clinical practice. Various excipients and concentrations were examined to achieve...
02. April 2017
Abstract Topical drug delivery systems provide localized drug action. A hydrophilic polymer such as polyvinyl alcohol is a multi-faceted excipient that can be used as a coating agent, lubricant, stability enhancer and viscosity-increasing agent. The objective of our study was to evaluate the use of polyvinyl alcohol polymer in preparing a topical gel with a diclofenac salt as the pharmaceutical active. The gel was characterized for its rheological and other properties and its effectiveness to...
22. March 2017
Abstract: Triterpene compounds like betulin, betulinic acid, erythrodiol, oleanolic acid and lupeol are known for many pharmacological effects. All these substances are found in the outer bark of birch. Apart from its pharmacological effects, birch bark extract can be used to stabilise semisolid systems. Normally, birch bark extract is produced for this purpose by extraction with organic solvents. Employing supercritical fluid technology, our aim was to develop a birch bark dry extract suitable...
26. January 2017
Abstract Thiolated polymers are a promising new group of excipients, but their stability against atmospheric oxidation has not been investigated in detail, and only a few efforts have been made to improve their stability. The oxidation of the thiol groups in solutions of thiolated polymers may result in a decrease of mucoadhesion and unpredictable in situ gelation. The aims of our work were to study the stability of aqueous solutions of thiolated polymers and the effects of stabilizing...
30. October 2016
Abstract Diclofenac topical formulations are often preferred for drug administration to patients who experience serious GIT problems. Absorption of the drug through the skin, however, can be challenging due to the natural protective feature of the stratum corneum (SC). In this article, fluid gels prepared from gellan gum were explored as a topical drug delivery vehicle. Rheological analysis of the formulations showed that it was possible to produce a topical gel with a viscosity and the...