- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. June 2018
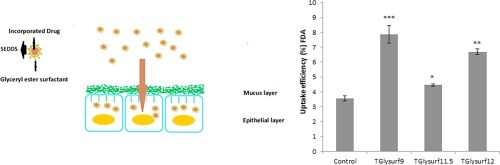
The aim of the study is the evaluation of the impact of glyceryl ester surfactants on cell permeating properties of SEDDS (self-emulsifying drug delivery systems). Methods SEDDS containing the glyceryl ester surfactants polyglyceryl-3-stearate (TGlysurf9), polyglyceryl-5-oleate (TGlysurf11.5) and glyceryl stearate citrate (TGlysurf12) were prepared and characterized regarding droplet size and zeta potential. Toxicity studies were performed on Caco-2 cells using resazuring assay. The...
29. May 2017
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) are lipid formulations that improve solubility and oral bioavailability of the incorporated drug with poor biopharmaceutical properties. As liquids they are traditionally filled into soft or hard capsules.
03. April 2017
Abstract: A novel supersaturable self-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SEDDS) of cyclosporine A (CyA)—a poorly water-soluble immunosuppressant—was constructed in order to attain an apparent concentration–time profile comparable to that of conventional SEDDS with reduced use of oil, surfactant, and cosolvent. Several hydrophilic polymers, including polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), were employed as precipitation inhibitors in the conventional SEDDS, which consists of corn...
29. March 2017
Aim The aim of this study was to evaluate the protective effect of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for therapeutic peptides towards intestinal proteases and reduced glutathione (GSH). Methods Sodium docusate was applied as anionic surfactant for hydrophobic ion pairing with leuprorelin (LEU), insulin (INS) and desmopressin (DES). The complexes were loaded into SEDDS that were characterized regarding droplet size distribution and zeta potential. The release profile of the peptides...
20. February 2017
Abstract Adsorption of lipid-based formulations, which are usually liquid, onto silicas has been extensively investigated in the past decade to convert them into solid dosage forms. There are conflicting reports on the ability of commercially available porous silicas, like Neusilin® US2, to release lipid formulations completely, especially after long-term storage. In this study, the release of a model drug, probucol, from different formulations of medium chain lipids and a surfactant,...
13. February 2017
Abstract The objective of this study is to enhance the dissolution properties of leflunomide, a class BCS-II drug by incorporating the self emulsifying (SE) form of the drug onto liquisolid systems in the form of tablets. Different formulae were prepared by dissolving leflunomide in PEG300 then forming SE systems using tween 80 as surfactant and either sesame oil and paraffin oil then adsorbing on powder excipients to form SE liquisolid powders. The prepared powders showed adequate flowability....
03. March 2016
Conversion of liquid and semisolid lipids into free flowing powders is an advantageous technique, as the carriers display high surface area, strong adsorption capacity, ease of processing, and ability to generate lipid loaded free flowing powders which can be converted to solid dosage forms like tablets and capsules. A combination of density, adsorption capacity and desorption is found to be of importance in the selection of the right adsorbent. Adsorbents like magnesium aluminium silicates...
06. December 2015