- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
16. August 2018
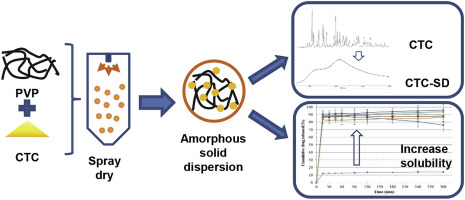
Chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CTC) has been reported as having low aqueous solubility, leading to a limitation in its administration in treatments. This study demonstrated a strategy to enhance the supersaturated solubility of CTC by amorphous solid dispersion (SD). CTC-SDs were prepared with hydrophilic polymers, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and copovidone using various preparation methods: water bath evaporation, speed vacuum evaporation, and spray drying. Physicochemical properties and...
15. March 2018
Salts of weakly basic active pharmaceutical ingredients are widely used to improve aqueous solubility and/or dissolution rate. However, these compounds are prone to precipitation due to the lower solubility of the un-ionized species at the higher pH in the intestinal region, and this can result in poor and/or variable absorption.
09. March 2018
The use of amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) to overcome poor drug solubility has gained interest in the pharmaceutical industry over the past decade. ASDs are challenging to formulate because they are thermodynamically unstable, and the dispersed drugs tend to recrystallize. Until now, most research on ASDs has focused on immediate-release formulations, supersaturation, and stability; only a few studies have recently reported on the manufacturing of sustained-release ASDs.
03. October 2017
Supersaturating drug delivery systems (SDDS), as solid dispersions (SDs), stand out among strategies to enhance bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. After oral administration, their dissolution in gastrointestinal fluids often leads to supersaturation, which drives to a rapid and sustained absorption.
01. October 2017
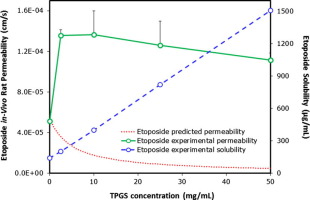
Vitamin E TPGS (TPGS) has both surfactant and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitory effects. While surfactants were previously found to cause solubility-permeability tradeoff, TPGS P-gp inhibitory effects may change this unfavorable interplay. The purpose of this research was to investigate the solubility-permeability interplay when using TPGS vs. amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) as oral drug delivery systems for the anticancer, P-gp substrate, lipophilic drug etoposide. The concentration-dependent...
05. September 2017
Abstract Amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) are probably the most common and important supersaturating drug delivery systems for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. These delivery systems are able to achieve and maintain a sustained drug supersaturation which enables improvement of the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs by increasing the driving force for drug absorption. However, ASDs often require a high weight percentage of carrier (usually a hydrophilic polymer) to...
22. June 2017
Discovery of several poorly water soluble drugs in the past decade has led to the need of developing a novel dosage form which increases the solubility of the drug and improves oral bioavailability.
19. April 2017
Abstract We developed a step-by-step experimental protocol using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), dynamic vapour sorption (DVS), polarized light microscopy (PLM) and a small-scale dissolution apparatus (μDISS Profiler) to investigate the mechanism (solid-to-solid or solution-mediated) by which crystallization of amorphous drugs occurs upon dissolution. This protocol then guided how to stabilize the amorphous formulation. Indapamide, metolazone, glibenclamide and glipizide were selected...
03. April 2017
Abstract: A novel supersaturable self-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SEDDS) of cyclosporine A (CyA)—a poorly water-soluble immunosuppressant—was constructed in order to attain an apparent concentration–time profile comparable to that of conventional SEDDS with reduced use of oil, surfactant, and cosolvent. Several hydrophilic polymers, including polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), were employed as precipitation inhibitors in the conventional SEDDS, which consists of corn...
08. March 2017
Abstract Poor aqueous solubility is a major concern for many new drugs. One possibility to overcome this issue is to formulate the drug as a high energy form, i.e. a metastable polymorph, an amorphous neat drug or a glass solution with polymers. In this study the dissolution properties of different solid state forms of carbamazepine, crystalline or amorphous drug, with or without either polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) or hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) and glass solutions of the drug with both...