- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
05. May 2018
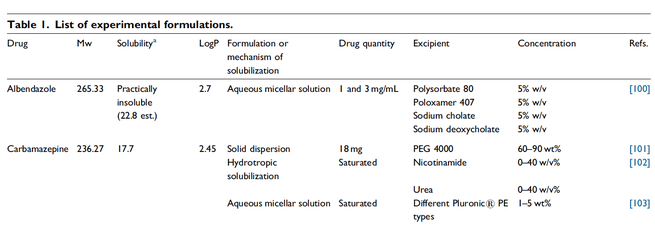
Along with the development of novel drug delivery systems the material science is also advancing. Conventional and novel synthetic or natural excipients provide opportunities to design dosage forms of the required features including their bioavailability.
19. April 2018
Cell-free permeation systems are gaining interest in drug discovery and development as tools to obtain a reliable prediction of passive intestinal absorption without the disadvantages associated with cell- or tissue-based permeability profiling. Depending on the composition of the barrier, cell-free permeation systems are classified into two classes including (i) biomimetic barriers which are constructed from (phospho)lipids and (ii) non-biomimetic barriers containing dialysis membranes. This...
14. February 2018
The aim of the current investigation was to develop solid lipid nanoparticles of olmesartan medoxomil using hot homogenization method to improve its oral bioavailability. Central composite design was applied to optimize the formulation variables; lipid X1 (Glyceryl monostearate) and surfactant X2 (Poloxamer: Tween 80).
05. February 2018
Candesartan cilexetil is an ester prodrug antagonist to angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) used in management of many cardiovascular diseases. The absolute bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil is about (14–40%). Therefore, the paper aim was to prepare and evaluate solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for candesartan cilexetil in order to improve its solubility, dissolution and stability. Solubility study was run in different vehicles to select the best excipients for dissolving
06. January 2018
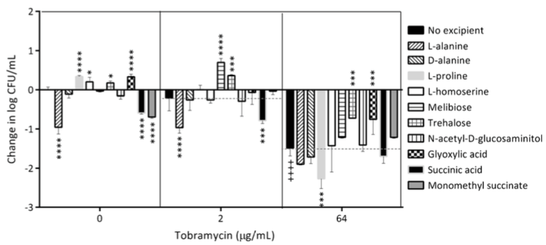
It is unknown if inactive pharmaceutical ingredients influence the activity of antibiotics they are co-formulated with. Recently it was found that materials acting as carbon nutrient sources for bacteria can promote bacterial dispersion from a biofilm and/or reverse the persister state of a subpopulation of bacteria within the biofilms. Both can make bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics.
15. August 2017
This study investigates the stability of typically complex multi-component hydrophilic solid dispersions that could be used in a clinical application.