- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
30. January 2018
Continuous Manufacturing Technology continues to gain importance in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Although traditional processes like direct compression, roller compaction, or wet granulation are used within the continuous lines, the requirement for ingredients may differ from traditional batch processing.
16. September 2017
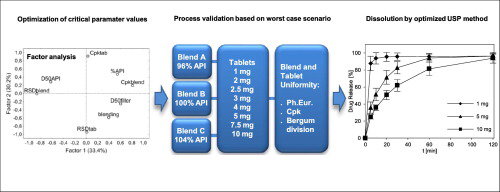
Abstract Warfarin is intensively discussed drug with narrow therapeutic range. There have been cases of bleeding attributed to varying content or altered quality of the active substance. Factor analysis is useful for finding suitable technological parameters leading to high content uniformity of tablets containing low amount of active substance. The composition of tabletting blend and technological procedure were set with respect to factor analysis of previously published results. The...
22. April 2017
Abstract Mini-tablets have potential applications as a flexible drug delivery tool in addition to their generally perceived use as multi-particulates. That is, mini-tablets could provide flexibility in dose finding studies and/or allow for combination therapies in the clinic. Moreover, mini-tablets with well controlled quality attributes could be a prudent choice for administering solid dosage forms as a single unit or composite of multiple mini-tablets in patient populations with swallowing...
10. April 2017
Abstract The aim of this study was to develop esomeprazole magnesium (EMZ-Mg) enteric-coated pellets and pellet-based tablets, as well as to investigate the effects of pellet size and compression method on acid tolerance, content uniformity, compressibility, and stability of preparations. This study used two types of pellet cores, namely, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) core with a particle size of 150–300 μm and sucrose core with a particle size of 600–700 μm. Enteric-coated pellets,...
24. March 2017
Abstract Recent work established polymer strip films as a robust platform for delivery of poorly water-soluble drug particles. However, a simple means of manipulating rate of drug release from films with minimal impact on film mechanical properties has yet to be demonstrated. This study explores the impact of film-forming polymer molecular weight (MW) and concentration on properties of polymer films loaded with poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Nanoparticles of griseofulvin, a model...
20. March 2017
Abstract Purpose A near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopic method was developed for real time analysis of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in blends from a continuous manufacturing process. The sampling and analytical errors of these determinations were estimated through variographic analysis. Methods Thirty-three calibration blends were prepared in laboratory scale equipment with a concentration range spanning from 70 to 130% of API target concentration. The NIR calibration model was...
06. February 2017
Abstract The purpose of this work was to assess the impact of continuous mixing on tablet critical quality attributes (CQAs) manufactured using a continuous, direct compression process. A nine run design of experiments (DoE) that bracketed the range of commercially relevant mixer speeds, mixer orientations, and mass flow rates was executed using a formulation containing a cohesive drug substance at relatively low drug load. Drug substance dispensed concentration using loss-in-weight feeders was...
13. December 2016
Abstract Previously, granulated lactose carriers were shown to improve uniformity and aerosolization of a low-dose model drug. In the present study, the blending uniformity and aerosol dispersion performance were assessed for 2 model drugs salbutamol sulfate (SS) and rifampicin (RIF), blended at high loadings (10% or 30% drug) with granulated lactose carriers. The model drug powders differed in particle size distribution, morphology, density, and surface energies. Content uniformity of RIF...
15. January 2016
A new formulation method for solid dosage forms with drug loadings from 0.65 ± 0.03% to 39 ± 1% (w/w) of acetaminophen (APAP) as a model drug has been presented. The proposed method involves the production of highly-porous lactose with a BET surface area of 20 ± 1 m2/g as an excipient using a templating method and the incorporation of drug into the porous structure by adsorption from a solution of the drug in ethanol. More
21. September 2015
Excipients do cause batch failures. But we need to ask: How often are they the culprit and can we elucidate what role excipient variability plays in this manufacturing fact of life? More