- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. November 2017
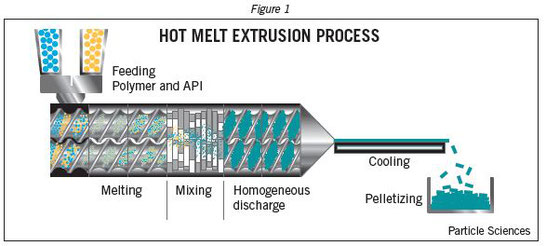
Amorphous solid dispersions (SDs) are considered as one of the most effective strategies for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. The active compound is dispersed in an inert carrier composed of a polymer and active excipients. Since the drug is amorphous, there is typically an increase in apparent solubility as well as dissolution rate. Various methods are employed for manufacturing of SDs, nevertheless, hot-melt extrusion (HME) has become one of the most common process techniques
09. October 2017
It is a well-known fact that the dissolution rate is higher for the amorphous form of a poorly soluble drug than from its various crystal forms. However, the amorphous state is inherently unstable and tends to recrystallise back into the poorly soluble form.
14. September 2016
Abstract This work investigates whether the solubility of poorly soluble compounds can be improved by using mesoporous magnesium carbonate (MMC) as the drug delivery system. A solvent evaporation method was used to load structurally diverse model drugs (celecoxib, cinnarizine and griseofulvin) into the pores of MMC. The drug-loaded carrier system was then characterized in terms of porosity, crystallinity, and release profiles by a variety of experimental techniques, including X-ray diffraction,...
11. September 2016
For the first time, researchers have revealed the nanostructure of the mesoporous magnesium carbonate Upsalite and pore size control was achieved without organic templates or swelling agents. By controlling the pore structure of the material the amorphous phase stabilization exerted on poorly soluble drug compounds can be tuned and the drug delivery rate can be tailored. More
16. November 2015
See also: First in-vivo biocompatibility study of Upsalite® is published!
30. June 2015
In a study published today in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (link), Professor Strømmes group shows, in collaboration with Associate Professor Christel Bergström's research in pharmacy, that release of pharmaceuticals from Upsalite® can be controlled with great precision by choosing the right size of Upsalite® particles. More
22. June 2015
By Gareth MacDonald+, 22-Jun-2015 Swedish scientists who developed the solubility enhancing nanotech excipient Upsalite say it can also be used to improve delayed release formulations. More See also: http://www.pharma-excipients.ch/2015/06/22/diffusion-controlled-drug-release-from-the-mesoporous-magnesium-carbonate-upsalite-abstract/
22. June 2015
In vitro drug release from well-defined particle-size fractions of the mesoporous magnesium carbonate material Upsalite® was investigated in detail using ibuprofen, a biopharmaceutics classification system class II drug, as the model compound. The weight of loaded drug corresponded to 30% of the weight of the carrier and the pores were filled to approximately 80%. More
11. April 2015
Johan Forsgren , Sara Frykstrand ,Kathryn Grandfield,Albert Mihranyan ,Maria Strømme Published: July 17, 2013DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068486 http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0068486