- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
29. September 2018
In this study, corn starch and ibuprofen are treated in Argon (Ar) plasma to enhance the wettability of the powders without using any additive or guest particle. The powder and pellets were exposed to the Ar plasma for different time intervals (5–20 min) at optimized pressure and voltage. While the morphological changes due to plasma exposure are captured by SEM, the AFM measurement shows the variations in surface roughness for both corn starch and ibuprofen powders. The XPS and surface...
15. June 2018
This study explores the influence of different synthesis methods and drying conditions in the preparation of sodium alginate-derivate xerogels presenting interesting disintegrant functionalities. Xerogels containing alginic acid (AA) or calcium alginate (CaA) and a mixture of both, AA/CaA, were isolated using two different drying methods oven and rotary evaporation. AA showed the best wettability behavior, in contrast to the rigid crosslinked CaA structure which showed a limited rate of water...
28. September 2017
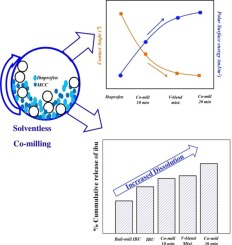
The wetting and dissolution of a BCS class II drug (Ibuprofen) is enhanced by solventless solid dispersion technique using co-milling. The co-milling is performed in a planetary ball mill using 1:1 wt. ratio of Ibuprofen (drug) and Microcrystalline cellulose, MCC (excipient).The improvement in wettability and dissolution after co-milling are compared with the raw ibuprofen, ball-milled ibuprofen without any excipient and v-blend mixture of ibuprofen with an excipient. The changes in crystal...
22. May 2017
Study of surface properties of mucoadhesive polymers and their blends.
•Estimation of the surface free energy for mucoadhesive polymers and their blends.
•Influence of polymer blends composition on their swelling process and wetting properties.
•Effect pH of model fluids on swelling of matrices containing mucoadhesive polymers.
08. May 2016
Objective: To investigate the modulation of the wettability of excipients by types of surfactants and its impacts on the disintegration of tablets and drug release. Materials and methods: The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of surfactants including sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (DTAB), cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) and polysorbate (Tween-20 and Tween-80) was obtained using the platinum ring method. Contact...