- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. May 2018
This study explores the methodology advised by healthcare professionals and the methods used by parents/carers to identify whether there is a best practice method for manipulation of 10 mg hydrocortisone tablets to provide an accurate dose to children. Bespoke surveys were used to identify methods recommended and used in manipulation of tablets. Hydrocortisone tablets were manipulated to provide a specified dose by both naïve participants and parents/carers. The accuracy of manipulation was...
02. March 2018
The selection and design of dosage form for the paediatric population is a real challenge. Part of that challenge is to deal with the diversity of the patient population (new born to adolescent) (CPMP, 2001) leading to specific patient compliance and acceptability. The choice of an age-appropriate formulation for children aged from 1 to 6 years old requires one to consider the ease of use of the formulation as well as the acceptability which will be mainly driven by palatability.
24. March 2017
Abstract Introduction: Most conventional drug delivery systems are not acceptable for pediatric patients as they differ in their developmental status and dosing requirements from other subsets of the population. Technology platforms are required to aid the development of age-appropriate medicines to maximize patient acceptability while maintaining safety, efficacy, accessibility and affordability. Areas covered: The current approaches and novel developments in the field of age-appropriate drug...
10. October 2016
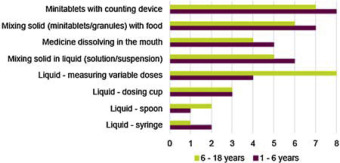
Abstract A lack of evidence to guide the design of age-appropriate and acceptable dosage forms has been a longstanding knowledge gap in paediatric formulation development. The Children’s Acceptability of Oral Formulations (CALF) study captured end-user perceptions and practices with a focus on solid oral dosage forms, namely tablets, capsules, chewables, orodispersibles, multiparticulates (administered with food) and mini-tablets (administered directly into the mouth). A rigorous development...
18. July 2015
10. July 2015
Children may be unable or unwilling to swallow medicines. In order to avoid or accommodate any such problems, parents may decide to administer medicines other than intended. The aim of this study was to investigate how parents administered four oral placebo formulations to infants and preschool children and how the applied methods correlated with child acceptability. More