- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
15. September 2018
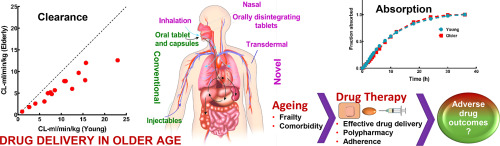
Both drug delivery performance and various age-related physical, mental and physiological changes can affect their effectiveness and safety in elderly patients. The many drug delivery systems developed over the years include recent novel transdermal, nasal, pulmonary and orally disintegrating tablet delivery systems that provide consistent, precise, timely and more targeted absorption. Certain drug delivery systems may be associated with suboptimal outcomes in the elderly because of the nature...
04. July 2018
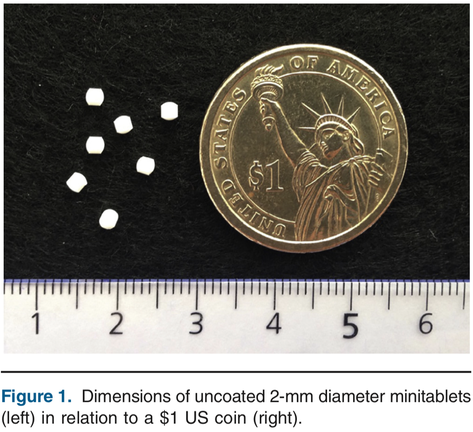
The objective of this study was to assess the acceptability and swallowability of several minitablets when administered as a unit dose compared with an equivalent dose of syrup in children aged 6 months to 5 years. Study design The acceptability and swallowability of multiple drug-free minitablets in comparison with glucose syrup was assessed in 372 children of 2 age groups (186 in age group 1 [6-23 months of age] and 186 in age group 2 [2-5 years of age]) in a randomized, 3-way, single...
07. June 2018
3D printing evolved as a promising technique to improve individualization of drug therapy. In particular, when printing sustained release solid dosage forms, as for instance implants, inserts, and also tablets, estimation of the drug release profile in vivo is necessary. In most cases, corresponding analyses cannot be performed at hospital or community pharmacies. Therefore, the present study aimed to develop a sustained release drug delivery system produced via 3D printing, which allows dose...
06. May 2018
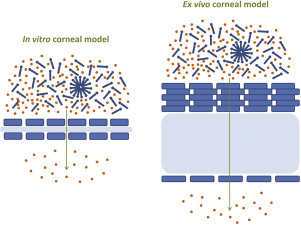
The objective of this study was to systematically investigate the effects of surface active ophthalmic excipients on the corneal permeation of ophthalmic drugs using in vitro(HCE-T cell-based model) and ex vivo (freshly excised porcine cornea) models. The permeation of four ophthalmic drugs (i.e., timolol maleate, chloramphenicol, diclofenac sodium and dexamethasone) across in vitro and ex vivocorneal models was evaluated in the absence and presence of four commonly used surface active...
27. April 2018
This article reviews regulatory considerations for companies wishing to develop drugs for delivery via the respiratory tract (e.g., by oral inhalation or intranasally) using molecules previously approved for a different therapeutic indication and/or a different delivery route. Conceptually, such repurposing has many medical and business advantages, but turning promising ideas into real products requires overcoming a number of practical challenges. Obtaining regulatory approval to market a...
06. September 2017
Abstract This review summarizes recent progress of the robust and smart hydrogels prepared from natural polymers including polysaccharides, proteins, etc. These hydrogels exhibit outstanding mechanical properties due to their nanofibrous aggregated microstructures and special crosslinking networks. Furthermore, these hydrogels show some smart stimuli-responsive behaviors triggered by pH, temperature, light, electricity and magnetism. Hopefully, these hydrogels derived from natural polymers with...
15. March 2017
Abstract The present study was designed to prepare and compare bio-adhesive pellets of panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) with hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), chitosan, and chitosan : carbomer, explore the influence of different bio-adhesive materials on pharmacokinetics behaviors of PNSbio-adhesive pellets, and evaluate the correlation between in vivo absorption and in vitro release (IVIVC). In order to predict the in vivo concentration-time profile by the in vitro release data of...
06. February 2017
Abstract Liquid adsorption on solid adsorbent carriers is an emerging technique for oral lipid-based drug delivery systems. The purpose of the current study is to convert liquid into solid self-emulsifying lipid formulations (SELFs) using an inorganic adsorbent Neusilin® grade US2 (NUS2) and investigate in vitro dissolution and digestion performance of the model antipsychotic compound risperidone. Methods The liquid SELFs were designed using various oils, nonionic surfactants and converted...
06. January 2017
Abstract Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) HiCelTM is native from cellulose, which is manufactured from wood pulp. Microcrystalline cellulose is made by hydrolysis reaction at temperature and pressure in presence of catalyst, which acts as reaction process increment. It is neutralized after completion of hydrolysis and intended to be used as to make microcrystalline cellulose powder. HiCelTM MCC is white crystalline, free flowing powder and medium in particles size. MCC is free flowing with...
16. December 2016
Abstract Spray-dried dispersions (SDDs) have become an important formulation technology for the pharmaceutical product development of poorly water-soluble (PWS) compounds. Although this technology is now widely used in the industry, especially in the early-phase development, the lack of mechanistic understanding still causes difficulty in selecting excipients and predicting stability of SDD-based drug products. In this review, the authors aim to discuss several principles of polymer science...