- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
26. September 2018
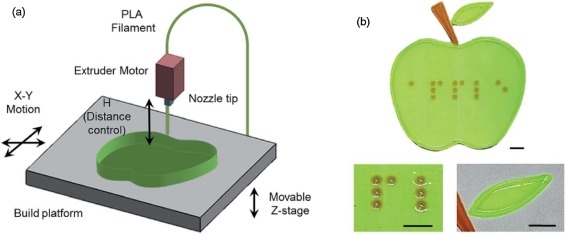
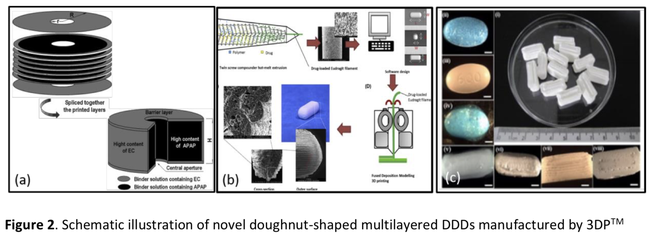
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is classified as a revolutionary, disruptive manufacturing technology. Cellulose (the most abundant natural polymer) and its many derivatives have been widely studied for many applications. The combination of 3D printing with cellulose-based feedstocks is therefore of critical interest. This review highlights many studies on 3D printing applications of plant-derived cellulose and its derivatives. Potential materials include cellulose ethers/esters,...
13. September 2018
Orodispersible films (ODFs) provide high application comfort due to rapid disintegration in the oral cavity. They increasingly found the approval of pharmaceutical research and development and were added to the European Pharmacopeia in 2012. The European Pharmacopeia explicitly demands disintegration testing for ODFs, but does not refer to a suitable method. The aim of this study was to collect and evaluate existing disintegration methods regarding their suitability to investigate different ODF...
02. September 2018
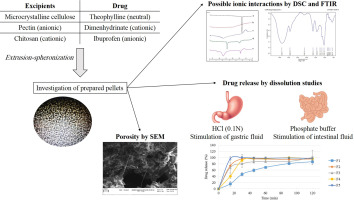
This study aimed to evaluate the potential of applying pectin and chitosan polysaccharides in pellet formulation. These biopolymers have advantages such as biocompatibility, low toxicity, low price and easy processing which make them interesting candidates for drug delivery purposes. Careful control of pellet porosity is essential to achieve an appropriate drug release profile. Replacing microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) with polysaccharides, especially pectin, leads to increased pellet...
01. September 2018
Flow properties of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) excipients, Avicel PH 101 and Avicel PH 102 have been compared by using Brookfield PFT. Afterwards, the effect of hydrophobic Silica R972 as glidant has been tested on both the excipients. Hand blending is done by mixing MCCs with hydrophobic silica R972 vigorously by SAC as an underlined basis for 10 minutes and the flow properties tests are performed. During the flow function test “as received” Avicel PH 102 shows better flow function...
22. August 2018
The effects of excipients on the accuracy of tablet subdivision are severely underinvestigated. In this study, placebo tablets were prepared using a combined mixture design of fillers and binders to evaluate the effect of these excipients on subdivision accuracy. The responses assessed were mass loss, mass variation, tablet fragmentation, and increased friability. Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCP) gave rise to more uniform and denser tablets than microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), thus...
07. July 2018
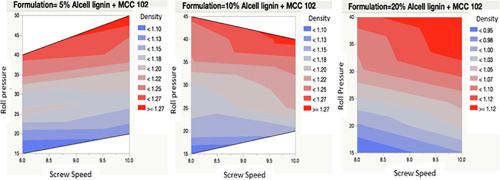
In this study, a process map was developed in an effort to improve the understanding of dry granulation of pharmaceutical excipients by roll compaction process, and to implement the quality-by-design (QbD) approach. Through development of the process map, a correlation was made between the critical process parameters (roll pressure, screw speed), and critical quality attributes (density of ribbons and granule size). This method reduces development time, quantity of materials required and cost....
08. May 2018
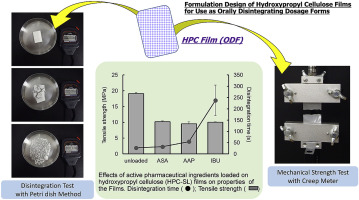
Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a water-soluble polymer used as a binder during pharmaceutical tableting and granulation. HPC is also known as a base material for pharmaceutical film by virtue of its film formability with excellent plasticity. The aim of this study was to assess the applicability of HPC to orally disintegrating film (ODF) and to investigate optimization of the ODF formulation of HPC. The effects of the molecular weight of HPC and the addition of active pharmaceutical...
06. May 2018
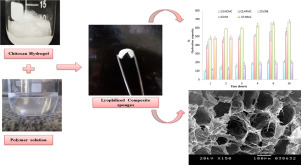
In the course of application and modernization of buccal dosage forms, lyophilized sponges for transmucosal drug delivery symbolize one of the most attractive approaches. Chitosan (CS) has been extensively investigated as a forming material of different buccal dosage forms including sponges. However, CS-based buccal delivery systems suffer from many limitations like weak adhesion strength and poor tensile properties. So, for the first time, the current study focused on the polymer blending...
17. April 2018
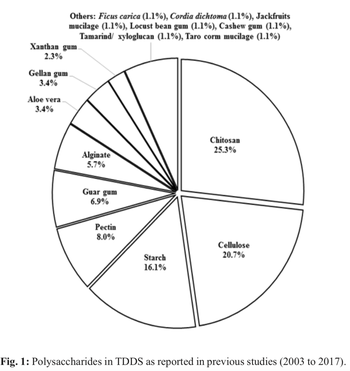
This article reviews various polysaccharides used in transdermal drug delivery system. The system provides continuous controlled delivery of active ingredients through human skin and into the blood stream. Poor penetration of most drugs into the skin has led to numerous studies being conducted to increase the permeability of such drugs. Currently, the interest to utilize natural polysaccharides in transdermal formulations has increased as an alternative to the synthetic materials. Structure...
04. April 2018
Wood-derived biopolymers have attracted great attention over the past few decades due to their abundant and versatile properties. The well-separated three main components, i.e., cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin, are considered significant candidates for replacing and improving on oil-based chemicals and materials. The production of nanocellulose from wood pulp opens an opportunity for novel material development and applications in nanotechnology. Currently, increased research efforts are...