- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
23. April 2018
The use of co-amorphous systems for solubility enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs has recently gained interest in the field of pharmaceutical technology. However, undesired co-amorphisation of a drug may lead to an alteration of the performance of the drug product, e.g. the previously observed co-amorphisation of indomethacin and arginine upon storage of tablets containing both components in an initially crystalline form at room temperature (RT) and 75 % relative humidity (RH)....
15. June 2017
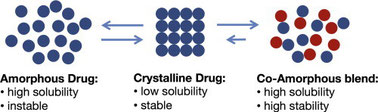
A promising approach to improve the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs and to overcome the stability issues related to the plain amorphous form of the drugs, is the formulation of drugs as co-amorphous systems.
24. March 2017
ABSTRACT Introduction: For almost two decades there has been intense debate about whether the amorphous solid state form could resolve the solubility problems and subsequent bioavailability issues of many small molecule drugs. Since the amorphous form is a high energy and unstable state of solid matter, any material in that form requires stabilization. Areas covered: This review examines the technologies being exploited to stabilize the amorphous state in co-amorphous formulations. The review...
12. February 2017
Abstract Co-amorphous systems is one of the attractive strategies used to enhance the dissolution rates of poorly soluble drugs. This strategy has an additional advantage as it has the ability to overcome stability issues that may arise from the conversion of a crystalline drug into its amorphous form. In this study, quench cooling was used to prepare co-amorphous forms of carbamazepine (CBZ) with saccharin (SAC), lactose (LAC) and gluconolactone (GLU) as carriers. Analytical techniques such as...
22. August 2016
Abstract Using amino acids (AA) as low molecular weight excipients in the preparation of co-amorphous blends with the aim to stabilize the drug in the amorphous form have been discussed in a range of studies. However, there is currently no theoretical consensus behind which AA would be a suitable co-former for a given drug. In this work, a fast screening process to assess the co-former feasibility in co-amorphous drug-AA blends has been developed on the basis of the amorphization kinetics upon...
04. July 2016
Abstract Molecular interactions were investigated within four different co-amorphous drug-amino acid systems, namely indomethacin−tryptophan (Ind−Trp), furosemide−tryptophan (Fur−Trp), indomethacin-arginine (Ind-Arg) and furosemide-arginine (Fur-Arg). The co-amorphous systems were prepared by ball milling for 90 minutes at different molar ratios and analyzed by XRPD and DSC. Interactions within the co-amorphous samples were evaluated based on the deviation between the actual glass...
12. June 2016
Introduction: For almost two decades there has been intense debate about whether the amorphous solid state form could resolve the solubility problems and subsequent bioavailability issues of many small molecule drugs. Since the amorphous form is a high energy and unstable state of solid matter, any material in that form requires stabilization. Areas covered: This review examines the technologies being exploited to stabilize the amorphous state in co-amorphous formulations. The review emphasizes...
13. April 2016
Co-amorphization has recently been shown to be a promising approach for stabilizing amorphous drugs and improving the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs. In this study, three basic amino acids were chosen as small molecular weight excipients to interact with the drug to form co-amorphous combinations. The co-amorphous combinations of valsartan (VAL) with l-histidine, l-arginine, and l-lysine were prepared by vibrational ball milling. Solid-state characterization with X-ray powder...
18. February 2016
Purpose Aiming to improve the dissolution rate of ezetimibe (EZE) and lovastatin (LOV) in a fixed dose combination (FDC), co-amorphous systems and ternary solid dispersions were prepared by quench cooling and spray drying, respectively. Methods Formulations were characterized through X-ray diffraction, modulated differential scanning calorimetry, infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and laser diffraction, and evaluated by ‘in vitro’ dissolution. Stability studies were...
26. January 2016
Co-amorphous drug delivery systems have recently gained considerable interest in the pharmaceutical field because of their potential to improve oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs through drug dissolution enhancement as a result of the amorphous nature of the material. A co-amorphous system is characterized by the use of only low molecular weight components that are mixed into a homogeneous single-phase co-amorphous blend. More