- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
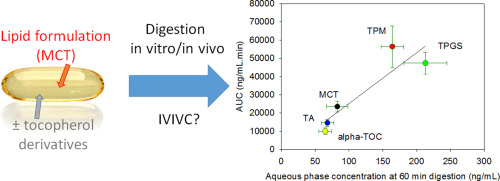
05. November 2017
Phosphorylated tocopherols are a new class of lipid excipients that have demonstrated potential in pharmaceutical applications. Their ability to solubilise poorly water soluble drugs indicates their potential utility in improving bioavailability of drugs where solubility limits their bioavailability.
29. March 2017
ABSTRACT: Control of elemental impurities in pharmaceutical materials is currently undergoing a transition from control based on concentrations in components of drug products to control based on permitted daily exposures in drug products.Within the pharmaceutical community, there is uncertainty regarding the impact of these changes on manufactures of drug products. This uncertainty is fueled in part by a lack of publically available information on elemental impurity levels in common...
13. August 2016
Abstract The majority of newly discovered oral drugs are poorly water soluble, and co-administration with lipids has proven effective in significantly enhancing bioavailability of some compounds with low aqueous solubility. Yet, lipid-based delivery technologies have not been widely employed in commercial oral products. Lipids can impact drug transport and fate in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through multiple mechanisms including enhancement of solubility and dissolution kinetics,...
09. May 2016
Aim The aim of this study is the development of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) differing in amounts of ester substructures and to evaluate their stability in presence of pancreatic lipase and protective effect against luminal enzymatic metabolism using leuprorelin as model peptide drug. Methods Hydrophobic leuprolide oleate was incorporated into three different SEDDS formulations and their stability towards pancreatic lipases was investigated utilizing a dynamic in vitro...
12. March 2016
Abstract: Cellulose ethers are usually used as secondary emulsifiers. Different types of commercial hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) have been used here as the main emulsifier of oil-in-water emulsions to probe their impact on the lipid digestibility under simulated intestinal conditions. The droplet size distribution and ζ-potential of the emulsions subjected to in-vitro lipolysis have been compared with that of control samples (non-digested). The lipolysis has been quantified over time by...
29. November 2015
An increasing number of newly discovered drugs are poorly water-soluble and the use of natural and synthetic lipids to improve the oral bioavailability of these drugs by utilizing the digestion pathway in-vivo has proved an effective formulation strategy. The mechanisms responsible for lipid digestion and drug solubilisation during gastrointestinal transit have been explored in detail, but the implications of drug precipitation beyond the potential adverse effect on bioavailability have...