- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
01. March 2018
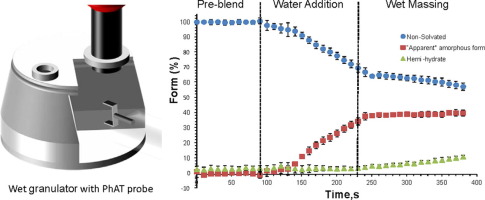
Form changes during drug product processing can be a risk to the final product quality in terms of chemical stability and bioavailability. In this study, online Raman spectroscopy was used to monitor the form changes in real time during high shear wet granulation of Compound A, a highly soluble drug present at a high drug load in an extended release formulation. The effect of water content, temperature, wet massing time and drying technique on the degree of drug transformation were examined.
08. November 2017
Co-processing is currently of interest in the generation of high-functionality excipients for tablet formulation. In the present study, comparative analysis of the powder and tableting properties of three co-processed starches prepared by three different methods was carried out. The co-processed excipients consisting of maize starch (90%), acacia gum (7.5%) and colloidal silicon dioxide (2.5%) were prepared by co-dispersion (SAS-CD), co-fusion (SAS-CF) and co-granulation (SAS-CG).
22. March 2017
Abstract: Triterpene compounds like betulin, betulinic acid, erythrodiol, oleanolic acid and lupeol are known for many pharmacological effects. All these substances are found in the outer bark of birch. Apart from its pharmacological effects, birch bark extract can be used to stabilise semisolid systems. Normally, birch bark extract is produced for this purpose by extraction with organic solvents. Employing supercritical fluid technology, our aim was to develop a birch bark dry extract suitable...
31. January 2017
Abstract The adsorption behavior of some metal ions (Pb, Mn, Mg, Zn and Ca) was studied on silicon dioxide nanoparticles, SiO2 NP, alone and its mixture with microcrystalline cellulose, MCC, powder (1:1) as drug carriers in pharmaceutical preparations. The effect of different conditions as temperature and pH on adsorption was investigated. It was found that upon increasing the temperature, the ability of the adsorbent material increases. The pH of the metal solution has the same effect as...
09. August 2016
Abstract This study involves the development of thin oral solvent cast films for the potential delivery of the proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole (OME) via the buccal mucosa for paediatric patients. OME containing films were prepared from ethanolic gels (1% w/w) of metolose (MET) with polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) (0.5% w/w) as plasticiser, and l-arg (0.2% w/w) as a stabilizer and dried in an oven at 40 °C. The blank and drug loaded films were divided into two groups, one group was subjected to...
06. July 2016
Abstract The phase transition of pharmaceutical excipients that can be induced by humidifying or heating is well-known to increase the hardness of orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs). However, these conditions are not applicable to drug substances that are chemically unstable against such stressors. Here, we describe a system which enhances the hardness of tablets containing water-insoluble polymers by using high-pressure carbon dioxide (CO2). On screening of 26 polymeric excipients,...
25. December 2015
The purpose of this investigation was to determine whether shellac, a naturally occurring material with enteric properties, could be processed in supercritical CO2 (sc-CO2) using the Particles from Gas Saturated Solution (PGSS) process and how process parameters affect the physico-chemical properties of shellac. More
22. November 2015
13. August 2015
Besides the known propolis biological activities, widely reported in many scientific studies, new findings in animal models have opened new fields for propolis application. Recently, there has been an increased interest in dried extracts based on natural products including propolis, as the product in the dry presentation shows several advantages. Therefore, standardizing a more soluble dry extract and allowing the production of human dosage forms are of great interest. In this context, this...