- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
15. September 2018
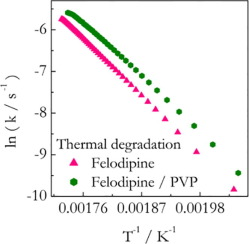
The present study explores the hypothesis that a polymer can affect the thermal stability of a drug in solid polymer-drug dispersions. The hypothesis is tested in a systematic fashion by combining isoconversional kinetic analysis with thermogravimetric measurements on several solid dispersions. Experimental systems involve three drugs: indomethacin (IMC), felodipine (FD), and nifedipine (ND) and their solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). It is found that PVP stabilizes IMC but...
25. August 2018
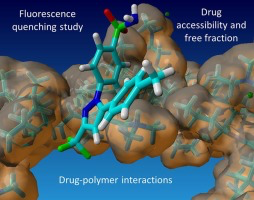
Solid dispersions (SDs) represent an important formulation technique to achieve supersaturation in gastro-intestinal fluids and to enhance absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. Extensive research was leading to a rather good understanding of SDs in the dry state, whereas the complex interactions in aqueous medium are still challenging to analyze. This paper introduces a fluorescence quenching approach together with size-exclusion chromatography to study drug and polymer interactions that...
18. August 2018
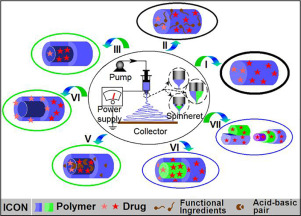
The development of oral dosage forms for poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is a persistent challenge. A range of methods has been explored to address this issue, and amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) have received increasing attention. ASDs are typically prepared by starting with a liquid precursor (a solution or melt) and applying energy for solidification. Many techniques can be used, with the emergence of electrospinning as a potent option in recent years. This...
16. August 2018
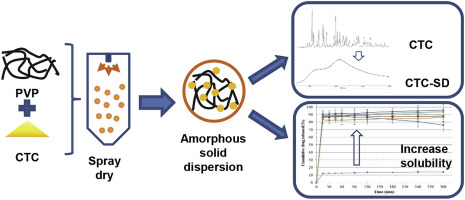
Chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CTC) has been reported as having low aqueous solubility, leading to a limitation in its administration in treatments. This study demonstrated a strategy to enhance the supersaturated solubility of CTC by amorphous solid dispersion (SD). CTC-SDs were prepared with hydrophilic polymers, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and copovidone using various preparation methods: water bath evaporation, speed vacuum evaporation, and spray drying. Physicochemical properties and...
07. June 2018
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEOX), a biocompatible polymer considered as pseudo polypeptide, was introduced as a potential alternative to the commonly used polymer, poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) for the preparation of solid dispersion with a poorly soluble drug. Glipizide (GPZ), a BCS class II model drug, was selected for solubility and dissolution rate study. GPZ-polymer solid dispersions and physical mixtures were characterized and investigated by X-Ray diffractometry, differential scanning...
26. May 2018
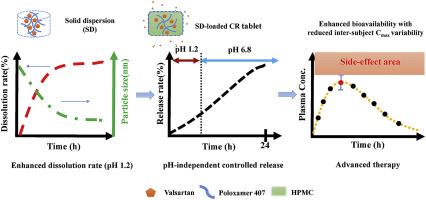
The aims of this work were to design pH-independent controlled release (CR) tablet containing nanonizing solid dispersion (SD) adsorbed on hydrophilic silica (Aeroperl® 300/30). Valsartan (VAL) was chosen to simultaneously modulate solubility and release rate due to its poor water solubility in low pH condition and short elimination half-life. Based on extensive equilibrium solubility and compatibility studies, poloxamer 407 was selected as a SD carrier. The melted mixtures of drug and...
24. January 2018
Considering everything involved with advancing a drug from discovery to a marketed product, the preparation of the film coating may seem like a simple step; just mixing powder and water. Yet it is an important step, and one of the essential steps we are regularly asked about.
11. January 2018
The oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can be improved by the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) where the API is dissolved in polymeric excipients. Desired properties of such ASDs like storage stability, dissolution behavior, and processability can be optimized by additional excipients. In this work, the influence of so-called low-molecular-weight excipients (LMWEs) on the phase behavior of ASDs was investigated.
28. September 2017
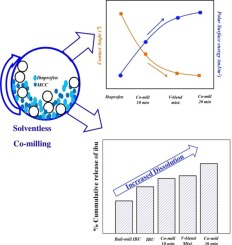
The wetting and dissolution of a BCS class II drug (Ibuprofen) is enhanced by solventless solid dispersion technique using co-milling. The co-milling is performed in a planetary ball mill using 1:1 wt. ratio of Ibuprofen (drug) and Microcrystalline cellulose, MCC (excipient).The improvement in wettability and dissolution after co-milling are compared with the raw ibuprofen, ball-milled ibuprofen without any excipient and v-blend mixture of ibuprofen with an excipient. The changes in crystal...
05. September 2017
Abstract Amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) are probably the most common and important supersaturating drug delivery systems for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. These delivery systems are able to achieve and maintain a sustained drug supersaturation which enables improvement of the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs by increasing the driving force for drug absorption. However, ASDs often require a high weight percentage of carrier (usually a hydrophilic polymer) to...