- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
21. June 2018
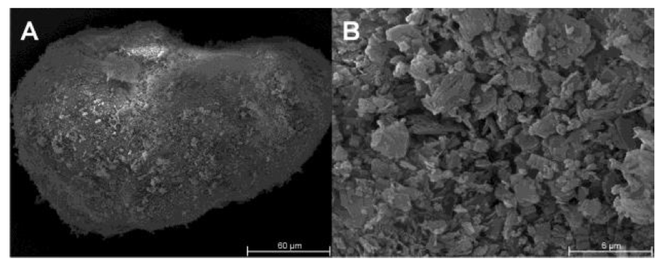
Tricalcium citrate (TCC) was characterized as a tableting excipient for direct compression (DC) and dry granulation (DG). SIGNIFICANCE: Brittle materials usually lead to tablets of inferior mechanical strength compared to plastic deforming materials. A brittle material exhibiting a high tabletability with the ability to retain that behaviour during recompression would represent a valuable alternative to the commonly used microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). METHODS: Tablets of TCC and other common...
05. June 2018
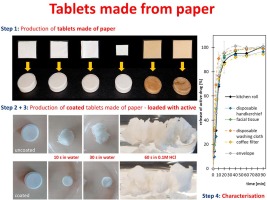
The possibility to compress ordinary paper into tablets was systematically investigated in this study. Results proved that tablets can be made from paper, independent of the type of paper used. The tablets appear shiny and with a smooth surface. The pharmaceutical quality was acceptable, i.e. all tablets fulfilled the requirements for tablets according to the European Pharmacopeia. Drug-loaded tablets were produced by compression of drug-loaded paper. Drug loading did not alter the...
27. February 2018
Adhesives can be defined as social substances capable to join permanently to surfaces, by an adhesive process. This process involves two dissimilar bodies being held in intimate contact such that mechanical force or work can be transferred across the interface. Since their early discovery by the Egyptians—3300 years ago—intensive research efforts have been made with the purpose of obtaining high-quality, biocompatible adhesives.
12. February 2018
Since decades, granulation is operational as a critical size enlargement process for powder agglomeration in tablet manufacturing. Dry granulation, melt granulation and wet granulation are some of the most common techniques utilized for granulation in the pharmaceutical industry.
03. January 2018
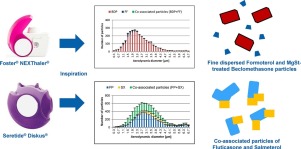
The in vitro aerosol performance of two combination dry powder inhaler (DPI) products, Foster® NEXThaler® and Seretide® Diskus® were investigated with single particle aerosol mass spectrometry (SPAMS). The in-vitro pharmaceutical performance is markedly different for both inhalers. Foster® NEXThaler® generates a higher fine particle fraction (FPF <5 μm) and a much higher relative extra fine particle fraction (eFPF <2 μm).
28. September 2017
A comprehensive model with all effective phenomena in drug release such as diffusion, swelling and erosion was considered. In this work, a mathematical model was developed to describe drug release from controlled release HPMC matrices as a favorable system in pharmaceutical industries. As a novel study, the impact of the MCC presence as a filler in tablet preparation process was considered in the mathematical model. In addition, we found that the volume expansion of these polymeric matrices did...
24. August 2017
Chemotherapy is one of the most conventionally used therapeutic interventions for treating various diseases. Chances of acquiring multidrug resistance in response to chemotherapeutic agents are exceedingly common among patients
17. August 2017
The work on the educational program for 2018 has started. Do you have any excipient related topics you would like to hear about next year in Puerto Rico? Your suggestions are very welcome!
26. June 2017
Poorly water soluble (PWS) drugs lack from good oral absorption, which limits their oral administration, the most common drug delivery route
19. May 2017
This study investigated the softening and erosive effects of various paediatric over-the-counter (OTC) oral liquids on deciduous teeth.