- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. September 2018
Orodispersible films (ODFs) provide high application comfort due to rapid disintegration in the oral cavity. They increasingly found the approval of pharmaceutical research and development and were added to the European Pharmacopeia in 2012. The European Pharmacopeia explicitly demands disintegration testing for ODFs, but does not refer to a suitable method. The aim of this study was to collect and evaluate existing disintegration methods regarding their suitability to investigate different ODF...
05. September 2018
This study aimed to enhance the dissolution rate of isradipine and to avoid the problem of first-pass metabolism using oral fast dissolving films (OFDFs). Isradipine was complexed with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) using the solvent co-evaporation technique to produce an isradipine inclusion complex with increased solubility. This complex was evaluated for its solubility and dissolution behavior compared with the free drug. Then, the inclusion complex was formulated in OFDFs. The...
15. August 2018
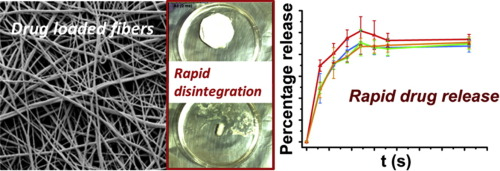
Increasing numbers of elderly people require multi-drug therapies. One route to improve adherence rates is to prepare fixed dose combinations (FDCs), in which multiple active ingredients are loaded into a single formulation. Here, we report the use of electrospinning to prepare fast-dissolving oral FDCs containing amlodipine besylate and valsartan, two drugs prescribed as FDCs for the treatment of hypertension. Electrospun fibers were prepared loaded with one or both drugs, using...
28. May 2018
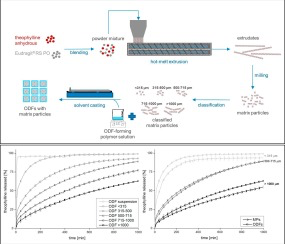
Orodispersible films (ODFs) are an advantageous dosage form to accomplish patient convenience and compliance in oral drug delivery. They provide a number of special application features, such as the ease of administration without water and suitability for patients with swallowing problems. However, this promising dosage form has been limited to immediate release formulations so far. The aim of this study was to develop a thin film produced by solvent casting, which is rapidly disintegrating...
17. May 2018
Current in vitro disintegration methods for polymeric films are qualitative and introduce significant user bias. The goal of these studies is to develop a novel, quantitative disintegration technique which can be used to characterize polymeric films in vitro. Methods A method was developed using a Texture Analyzer instrument to evaluate film disintegration. Solvent-casted, clinically advanced, anti-HIV, vaginal films as well as marketed vaginal films were used throughout these studies. Method...
31. January 2018
Multiple brands of the same active ingredient may be available for the same strength, administration route and dose form. Generic brands needs to demonstrate bioequivalence to the originator brand, but the appearance of the generic and originator brands are not required to match.
20. April 2017
Abstract The individualization of solid dosage forms to realize a flexible therapy for all patient groups is a topic which increasingly gains importance in pharmaceutical research. The goal of this study was to develop a nanoparticulate, instant orodispersible film (iODF) powder which can easily be reconstituted in water to cast ODFs containing an individualized concentration of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). It was shown that the processing of the film casing mass to iODF powders...
15. March 2017
Abstract Composite films were sprayed from mixtures of water soluble hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and either nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) or cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Fiber diameter was similar for both nanocelluloses but fiber length was several μm for NFC and about 200 nm for CNC. Films were characterized for morphology, swelling, mass loss and transport properties. NFC-HPMC films swelled less than CNC-HPMC films; with a HPMC content of 20 wt% NFC-HPMC and CNC-HPMC films...
08. March 2017
Abstract An experimental design was established in order to optimize the mechanical properties of two oral film formulations intended for oral delivery of bioactive compounds. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and gelatin type A (GelTA) were selected as polymeric matrix. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that caffeine crystals were homogeneously dispersed onto oral film matrix. Fourier-transform infrared analysis did not indicate formation of new chemical entities. USP modified dissolution assay...
06. February 2017
ABSTRACT This article presents a preformulation study of isolated poly(vinyl acetate) films with the addition of hyaluronic acid (HA). The films were prepared with the solvent evaporation method and evaluated according to macroscopic, morphologic, structural, water vapor transmission (WVT), swelling index (Si%), and thickness measurements and thermal analyses. The addition of HA resulted proportional reductions in the thickness, transparency, and flexibility and increased WVT rates and Si%....