- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
29. September 2018
Appropriate lubrication is important in tablet manufacturing as it lowers punch sticking propensity and protects tooling by reducing friction between die wall and tablet during tablet manufacturing. Most commercial lubricants negatively impact tabletability and dissolution. A delicate balance is usually attained by trial and error to identify the optimal level of lubricant in a tablet formulation. In this work, we have evaluated the effectiveness of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), a surfactant, as...
09. May 2018
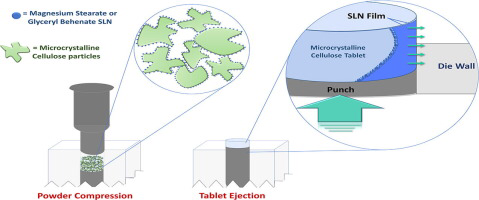
The aim of this study was to develop solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and introduce them into a direct compression process to evaluate their lubricant properties. The study consisted of preparing glyceryl behenate SLN (Compritol® 888 ATO) by hot dispersion, and magnesium stearate SLN by a novel nanoprecipitation/ion exchange method. The ejection force was measured for nanosystems and raw materials in a formulation typically used for direct compression. The smallest particle sizes obtained were...
06. September 2017
Abstract External lubrication is a useful method which reduces the adhesion of powder to punches and dies by spraying lubricants during the tableting process. However, no information is available on whether the tablets prepared using an external lubrication system can be applicable for a film coating process. In this study, we evaluated the adhesion force of the film coating layer to the surface of tablets prepared using an external lubrication method, compared with those prepared using...
05. September 2017
Abstract External lubrication is a useful method which reduces the adhesion of powder to punches and dies by spraying lubricants during the tableting process. However, no information is available on whether the tablets prepared using an external lubrication system can be applicable for a film coating process. In this study, we evaluated the adhesion force of the film coating layer to the surface of tablets prepared using an external lubrication method, compared with those prepared using...
20. July 2016
Abstract The purpose of this work was to develop a multiparticulate system exploiting the pH-sensitive prop- erty and biodegradability of calcium alginate beads for intestinal delivery of ceftriaxone sodium (CS). CS was entrapped in beads made of sodium alginate and sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), acacia, HPMC K4M and HPMC K15M as drug release modifiers. Beads were pre- pared using calcium chloride as a cross-linking agent, followed by enteric coating with cellulose acetate phthalate...
09. February 2016
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of different hydrophilic polymers on the swelling, bioadhesion and mechanical strength of hydrocolloid wound dressings (HCDs) in order to provide an appropriate composition for a hydrocolloid wound dressing system. In this study, the HCDs were prepared with styrene-isoprene-styrene copolymer (SIS) and polyisobutylene (PIB) as the base using a hot melting method. Additionally, numerous SIS/PIB-based HCDs were prepared with six...
10. November 2015
Tablets containing metoprolol succinate and Compritol®888ATO in the ratio of 1:2 yielded the desired sustained release profile in phosphate buffer pH 6.8 when evaluated using USP type II paddle apparatus and was selected as the optimized formulation. Robustness of optimized formulation was assessed by studying the effect of factors like varying source of metoprolol succinate and Compritol®888ATO, compression force and hydroalcoholic dissolution medium on the release profile. No significant...
08. August 2015
The aim of this study was to design a local, floating, mucoadhesive drug delivery system containing metronidazole for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Face-centered central composite design (with three factors, in three levels) was used for evaluation and optimization of in vitro floating and dissolution studies. Sodium alginate (X1), low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose (L-HPC B1, X2) and sodium bicarbonate (X3) concentrations were the independent variables in the development of...
20. June 2015
The effect of incorporating the lipidic medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) into polymeric film-forming systems (FFS) for topical drug delivery has been evaluated. First, the in vitro release of betamethasone-17-valerate (BMV), a representative dermatological drug, was determined from FFS comprising either hydrophobic polyacrylate co-polymers, or hydrophilic hydroxypropyl cellulose, with and without MCT. More