- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
07. September 2018
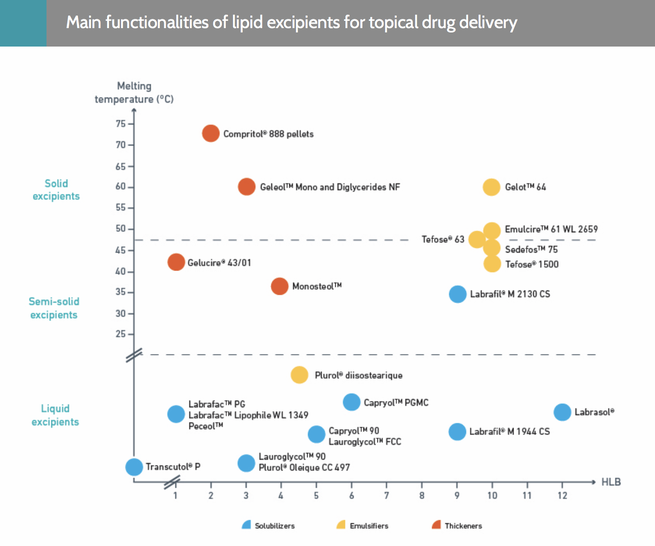
Lipid excipients for topical drug delivery include solubilizers, emulsifiers and viscosity modifying agents. Emulsifiers are designed for challenging formulations and deliver excellent texture and sensorial properties. Solubilizers provide skin penetration enhancement and viscosity agents stabilize formulations
16. August 2018
Vaginal drug delivery is a promising route for the treatment and prevention of local and systemic diseases such as genital herpes or AIDS. Suitable excipients must be selected to optimize the residence time of formulations in vaginal mucosa and could be included in the formulation. Many polymers are excellent choices for the development of vaginal drug delivery systems due to their properties of mucoadhesion, biocompatibility and biodegradability. These polymers swell in the aqueous medium of...
08. August 2018
Polymeric gels have emerged as promising vehicles for drug delivery across the skin. Stratum corneum, the topmost layer of the skin, does not allow hydrophilic and high molecular weight drugs to permeate without enhancing techniques. A number of enhancement techniques are being developed to increase the transdermal drug permeation. The transdermal route has many advantages and has therefore evolved as an attractive and convenient alternative to the existing routes of drug delivery that causes...
27. October 2016
Abstract Mucoadhesive in situ gelling systems (soluble gels) have received considerable attention recently as effective stimuli-transforming vectors for a range of drug delivery applications. Considering this fact, the present work involves systematic formulation development, optimization, functional evaluation and ex vivo performance of thermosensitive soluble gels containing dexamethasone 21-phosphate disodium salt (DXN) as the model therapeutic. A series of in situ gel-forming systems...
30. August 2016
Abstract In situ -gelling systems has the great potential in the wide areas of drug delivery. The application areas of such systems are broad and these systems can be formulated not only as gels but also as in situ gelling nanospheres, microspheres and liposomes. To overcome the drawbacks associated with conventional drug delivery systems and take advantages of both solutions and gels, such as accurate dosing, ease of administration of the former and longer precorneal residence of the latter, a...