- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
10. May 2018
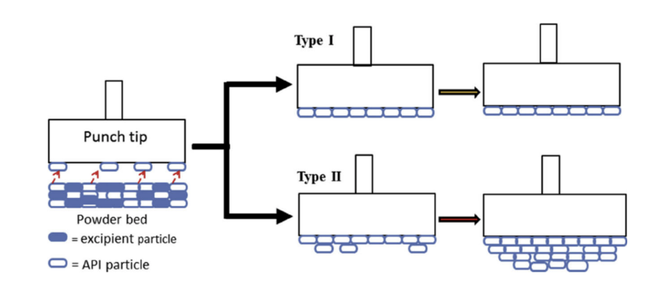
Purpose To investigate how excipient matrix affects punch sticking propensity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), with the focus on the effect of bonding interactions between API-API (F2) and API-excipient (F3). Method Sticking kinetics of direct compression formulations, consisting of 20% of celecoxib (CEL) or ibuprofen (IBN) indifferent excipient matrices, i. e., microcrystalline cellulose (Avice l PH102 and Avicel PH105 dry coated with nano-sized silica (PH105(n)), hypromellose (K15...
19. February 2018
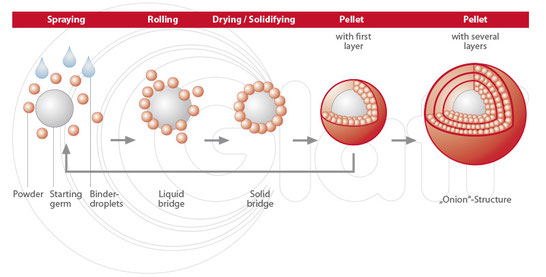
The objective of this study was to assess the efficacy and the capability of a novel ethylcellulose-based dry-coating system to obtain prolonged and stable release profiles of caffeine-loaded pellets. Lauric and oleic acids at a suitable proportion were used to plasticize ethylcellulose. The effect of coating level, percentage of drug loading, inert core particle size, and composition of the coating formulation including the anti-sticking agent on the drug release profile were fully...
15. January 2018
In line with the increasing demand for sustainable packaging materials, this contribution aimed to investigate the film-forming properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to correlate its chemical structure with film properties. The roles played by substitution degree (SD) and molecular weight (Mw) on the mechanical and water barrier properties of HPMC films were elucidated.
09. January 2018
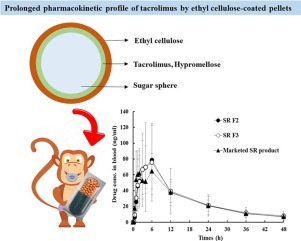
A novel once-a-day sustained-release (SR) system of tacrolimus (FK506), a poorly water-soluble immunosuppressive agent, was designed employing ethyl cellulose (EC) polymer as release retardant. Drug (5 mg) was layered onto sugar spheres (518.3 mg) with hypromellose (5 mg), to transform the drug from a crystalline to an amorphous form.
12. December 2017
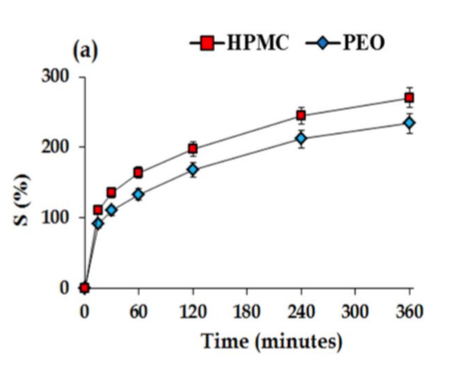
The aim of the present investigation was to understand the swelling behaviour of HPMC and PEO-based matrices and to evaluate the impact of porosity on the swelling kinetics. It was noticed that the HPMC has higher swelling rates but both undergo diffusion oriented swelling mechanism.
07. August 2017
Formulation of gliclazide in the form of extended- release tablet in 30 and 60 mg dosage forms was performed using hypromellose (HPMC K4M) as a retarding agent. Drug-release profiles were investigated in comparison with references Diamicron MR 30 and 60 mg tablets.
03. July 2017
A modified coaxial electrospinning for creating hypromellose-based composite fibers.
Quantitative analyses of Taylor cone and straight fluid jet during electrospinning.
Amorphous hydrophilic nanocomposites consisting of multiple components.
Improved performances about the fast dissolution of poorly water-soluble drug.
12. February 2017
Abstract In this study, hypromellose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) stable submicronic particles loaded with a soy isoflavones extract, have been obtained by nano spray drying technology. HPMCAS has been used as excipient able to increase both stability and supersaturation levels of the active ingredients hence able to enhance skin penetration performance of genistein and daidzein. The influence of polymer/extract ratio as other process variables, on particle size, morphology and permeation...
09. August 2016
Abstract The aim of this study is to present the possibility of using of co-processed dry binders for formulation of matrix tablets with drug controlled release. Hydrophilic matrix tablets with tramadol hydrochloride, hypromellose and different co-processed dry binders were prepared by direct compression method. Hypromelloses Methocel™ K4M Premium CR or Methocel™ K100M Premium CR were used as controlled release agents and Prosolv® SMCC 90 or Disintequik™ MCC 25 were used as co-processed...
25. January 2016
The purpose of the present work was to prepare multiparticulate drug delivery systems for oral administration of a poorly soluble drug such as itraconazole (ITZ). Multiparticulate systems were prepared by extrusion/spheronization technique using a mix of crospovidone, low viscosity hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, micronized drug and water. More