- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. September 2018
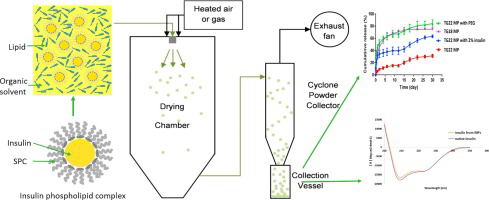
The study aimed at investigating the potential of spray drying method for encapsulation of protein drugs into solid lipid microparticles (MP) and evaluating effects of excipients on encapsulation and release of protein from MP. After transformation of model protein insulin to insulin-phospholipid complex, it was dissolved together with lipid excipients in organic solvent, which was spray-dried to form solid lipid MP. Polymeric MP with D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) were prepared similarly....
24. August 2018
In today's drug development world, combinatorial chemistry, high-throughputscreening, and genomics have provided a technologic platform that produces a large number of new chemical entities withtherapeutic potential each year. Its outcome the new chemical entities shifted towards higher molecular weight and increasing lipophilicity that results in poor water solubility which primarily affectsthe bioavailability of orally administered drugs. Hence, the poor aqueoussolubility not only limits the...
13. November 2017
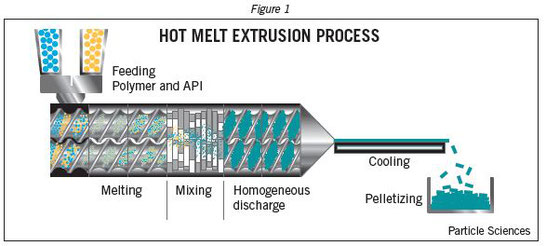
Amorphous solid dispersions (SDs) are considered as one of the most effective strategies for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. The active compound is dispersed in an inert carrier composed of a polymer and active excipients. Since the drug is amorphous, there is typically an increase in apparent solubility as well as dissolution rate. Various methods are employed for manufacturing of SDs, nevertheless, hot-melt extrusion (HME) has become one of the most common process techniques
01. November 2017
Poor solubility of drugs has always been an issue for formulation scientists thus the search for novel excipients or techniques is an ever-important field in the pharmaceutical developments. Besides the conventional solubilizers or pH adjusters and methods in the past decades particle size reduction is one of the new techniques to enhance the solubility of poorly water soluble drugs.
26. October 2017
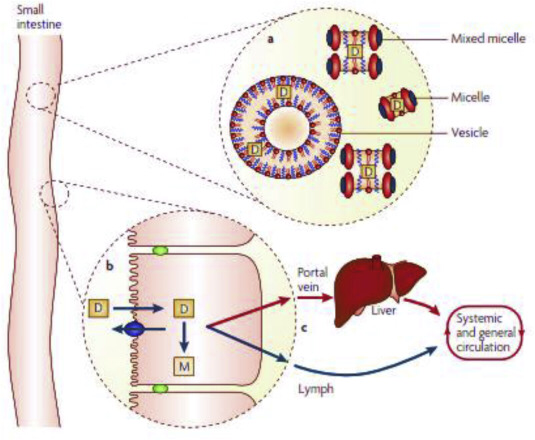
Lipid-based formulations (LBFs) can be effective oral drug delivery systems for poorly water-soluble chemical entities, provided they are designed with careful selection of the excipients, based on their role in the delivery system and in relation to the drug properties [1]. LBFs comprise four types of formulations (type I, II, III A and B, IV) containing mixture of oils, surfactants and hydrophilic cosolvents, some of which are able to self-emulsify in contact with the gastrointestinal medium...
20. October 2017
This article reviews the causes of poor bioavailability for drugs. It provides an introduction to lipid-based drug delivery systems, and how the formulation approach can be used to overcome impediments to good bioavailability of therapeutic actives, including poor water solubility, low permeability, and degradation by stomach acid or enzymes in vivo.
13. October 2017
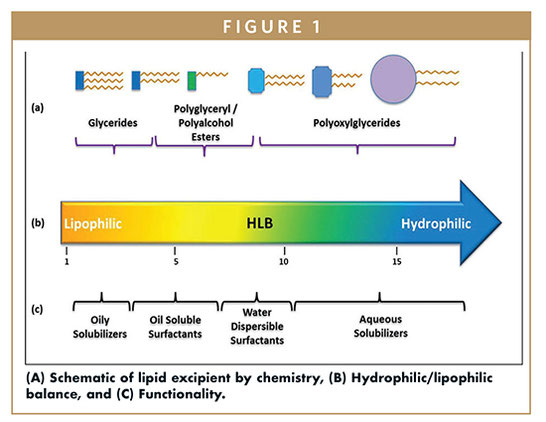
The majority of New Chemical Entitities (NCEs) being considered for therapeutic applications are BCS Class II, Class III, or Class IV, indicating that these potential Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) will exhibit solubility and/or permeability challenges. Functional lipids are one of the most widely employed excipient classes utilized in overcoming both solubility and permeability challenges. Many API’s which are insoluble in aqueous media can be emulsified in functional lipids...
07. October 2017
The aim of this work was to develop an innovative drug delivery system potentially useful for the local delivery of Bisphosphonates to bone tissue. We propose the use of Solid Lipid Microparticles (MPs), up to now mainly used for oral and topical drug delivery, as carrier for bisphosphonates due to the favourable biocompatibility and lower toxicity of the lipids compared with many polymers. The delivery platform consisted of a biomimetic α-tricalcium phosphate-gelatin cement (CPC) enriched...
03. October 2017
Components of the ocular surface synergistically contribute to maintaining and protecting a smooth refractive layer to facilitate the optimal transmission of light. At the air–water interface, the tear film lipid layer (TFLL), a mixture of lipids and proteins, plays a key role in tear surface tension and is important for the physiological hydration of the ocular surface and for ocular homeostasis. Alterations in tear fluid rheology, differences in lipid composition, or downregulation of...
06. September 2017
Abstract: Liquid crystal (LC)-forming lipids represent an important class of biocompatible amphiphiles and their application extends to cosmeceutical, dietary, and pharmaceutical technologies. In the present study, we aimed to develop strategies for designing and optimizing oral and topical LC formulations by evaluating their in vitro and in vivo drug absorption performances. C17-Monoglycerol ester (MGE) was used as a LC-forming lipid. p-Amino benzoic acid, methyl PABA, ethyl PABA, and sodium...