- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. December 2017
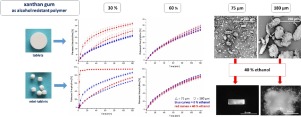
The vulnerability of controlled release formulations when co-ingested with alcohol represents a current major concern of regulatory agencies. Dose dumping might occur when drugs and/or excipients exhibit higher solubility in ethanolic solutions compared to water.
12. December 2017
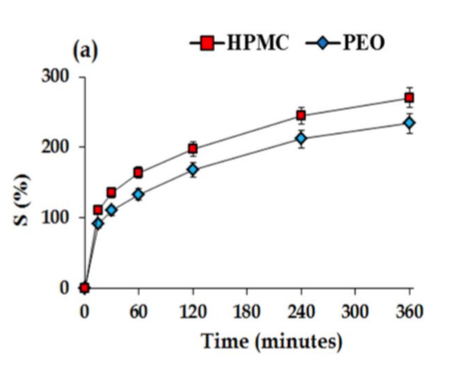
The aim of the present investigation was to understand the swelling behaviour of HPMC and PEO-based matrices and to evaluate the impact of porosity on the swelling kinetics. It was noticed that the HPMC has higher swelling rates but both undergo diffusion oriented swelling mechanism.
26. July 2017
The aim of this study was to evaluate the suitability of saturated phosphatidylcholine (Phospholipon® 90H) as extended release excipient in matrix tablets for three model drugs with different aqueous solubility (theophylline, caffeine and diprophylline)
15. June 2017
This pre-formulation study assays the capacity of the polyesteramide PADAS, poly (L-alanine-dodecanediol-L-alanine-sebacic), as an insoluble tablet excipient matrix for prolonged drug release.
15. June 2017
High amylose starch (HAS) was retrograded by two different methods. The physicochemical properties of the retrograded materials were evaluated and structural changes were highlighted.
12. May 2017
The aim of this study was to develop controlled-release matrix tablets of ketoprofen (K) and dexketoprofen trometamol (DK-T), investigating a new application of the polymer poly (L-alanine-dodecanediol-L-alanine-sebacic) (PADAS). The influence on drug release of the type of filler (lactose, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose or dibasic calcium phosphate) and of the polymer/filler proportion was also investigated.