- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. May 2018
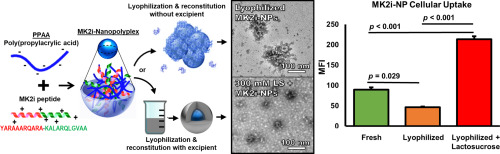
Herein, excipients are investigated to ameliorate the deleterious effects of lyophilization on peptide-polymer nano-polyplex (NP) morphology, cellular uptake, and bioactivity. The NPs are a previously-described platform technology for intracellular peptide delivery and are formulated from a cationic therapeutic peptide and the anionic, pH-responsive, endosomolytic polymer poly(propylacrylic acid) (PPAA). These NPs are effective when formulated and immediately used for delivery into cells and...
23. January 2018
Glucagon is a peptide hormone used for the treatment of hypoglycemia; however, its clinical potential is limited by its insolubility and instability in solution. Herein, the encapsulation, stabilization, and release of glucagon by trehalose glycopolymer nanogels are reported. Methacrylate-functionalized trehalose is copolymerized with pyridyl disulfide ethyl methacrylate using free radical polymerization conditions to form trehalose glycopolymers with thiol-reactive handles.
11. January 2018
Nanoparticles or microparticles created by physical complexation between two polyelectrolytes may have a prospective use as an excipient for oral insulin administration. Natural polymers such as tragacanth, alginate, dextran, pullulan, hyaluronic acid, gelatin and chitosan can be potential candidates for this purpose. In this research, insulin particles were prepared by the inclusion of insulin into a tragacanth hydrogel.
10. July 2017
Poster by Glatt Pharmaceutical Services & Credentis AG @EUPFI Congress in Warshaw -
01. May 2017
Recently nanoparticle-based vaginal drug delivery formulations have been acquiring great attention for the administration of peptide based-vaccines or microbicides to prevent or treat sexually transmitted diseases.
16. March 2017
Abstract Microneedles (MNs) have been investigated as a minimally-invasive delivery technology for a range of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Various formulations and methods for coating the surface of MNs with therapeutics have been proposed and exemplified, predominantly for hydrophilic drugs and particulates. The development of effective MN delivery formulations for hydrophobic drugs is more challenging with dosing restrictions and the use of organic solvents impacting on both the...
14. February 2017
Abstract There is a need to understand the nature of aggregation of cyclodextrins (CDs) with guest molecules in increasingly complex formulation systems. To this end an innovative application of Taylor dispersion analysis (TDA) and comparison with dynamic light scattering (DLS) have been carried out to probe the nature of ICT01-2588 (ICT-2588), a novel tumor-targeted vascular disrupting agent, in solvents including a potential buffered formulation containing 10% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin....
08. February 2017
Oral delivery of therapeutic peptides has been a constant source of frustration for delivery and formulation scientists over the last 50 years. Peptides are poorly absorbed via the oral route due to digestion and poor movement across the gut wall. For a long time the problem was limited to insulin and the non-peptide heparin, but today there are 60+ peptide drugs marketed worldwide, the majority of which are delivered using needles. Effort to enable more convenient oral delivery is associated...
15. December 2016
Abstract There is ample evidence that pharmaceutical excipients, which are supposed to be pharmacologically inactive, have an impact on drug metabolism and efflux transport. So far, little is known whether they also modulate uptake transporter proteins. We have recently shown that commonly used solubilizing agents exert significant effects on the function of organic anion uptake transporting polypeptides. Therefore, we investigated in this study the influence of frequently used pharmaceutical...
14. August 2016
Abstract A multiple-unit formulation for time-dependent colonic release of insulin was obtained by coating insulin and sodium glycocholate immediate-release minitablets with: i) Methocel® E50, a low-viscosity hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (inner coating); ii) 5:1 w/w Eudragit® NE/Explotab® V17, a mixture of a neutral polymethacrylate with a pore-forming superdisintegrant (intermediate coating); iii) Aqoat® AS, enteric-soluble hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (outer coating)....