- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
12. December 2017
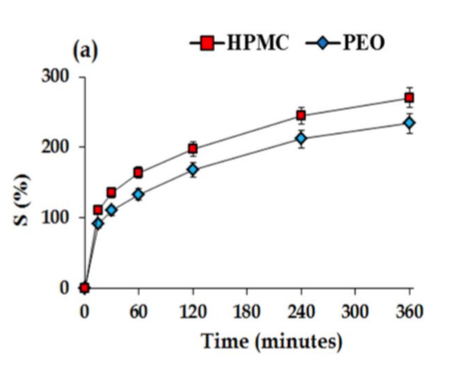
The aim of the present investigation was to understand the swelling behaviour of HPMC and PEO-based matrices and to evaluate the impact of porosity on the swelling kinetics. It was noticed that the HPMC has higher swelling rates but both undergo diffusion oriented swelling mechanism.
14. February 2017
Abstract In controlled porosity osmotic pumps (CPOP), usually finding a single solvent with a capability to dissolve both film former (hydrophobic) and pore former (hydrophilic) is extremely challenging. Therefore, the aim of the present investigation was to tackle the issue associated with controlled porosity osmotic pump (CPOP) system using nano-suspension coating method. In the present study 4-Amino pyridine was used as a highly water soluble drug. In this method, a hydrophilic pore former...
14. January 2017
Abstract The main purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of moisture content (MC) of different deformation granules (brittle, plastic, and elastic) and compression pressure (CP) on the physical properties of tablets. A general full factorial design was used with three blocks (deformation property of excipient) and two control factors: MC and CP. Lactose monohydrate (LM), microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), and corn starch (CS) were selected as brittle, plastic, and elastic...
08. November 2016
Abstract This study addresses the quantitative influence of 12 different materials (active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients as surrogate active pharmaceutical ingredients) on the critical quality attributes of twin screw granulated products and subsequently produced tablets. Prestudies demonstrated the significant influence of the chosen model materials (in combination with crospovidone) on the disintegration behavior of the resulting tablets, despite comparable tablet porosities. This...
01. October 2016
Abstract Flashing at tablet edges, an inevitable phenomenon when tableting a plastically deforming material under a high pressure, can introduce significant errors to tablet density and porosity determinations due to overestimated tablet thickness when tablet were measured out-of-die. Errors in tablet density determination also lead to errors in true density obtained by the Sun method, which is suitable for water-containing solids. Errors in true density and tablet porosity propagate to...
15. June 2016
Abstract In this study, terahertz time-domain spectroscopic (THz-TDS) technique has been used to ascertain the change in the optical properties, as a function of changing porosity and mass fraction of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), of training sets of pharmaceutical tablets. Four training sets of pharmaceutical tablets were compressed with microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) excipient and indomethacin API by varying either the porosity, height, and API mass fraction or all three tablet...
13. June 2016
The influence of relative humidity in the pan during coating on polymer deposition and film formation was investigated. Four tablet substrates, differing in hydrophobicity, porosity, and surface roughness, were prepared and coated with Eudragit® RS/RL 30 D (8:2 ratio). The spray rate and atomization air pressure were varied to create two distinct micro-environmental conditions in the coating pan. PyroButton data logging devices placed directly in the pan were found to more accurately reflect...
04. June 2016
A full factorial design of experiments was used to study the effect of blend shear strain on the compaction process, relative density and strength of pharmaceutical tablets. The powder blends were subjected to different shear strain levels (integral of shear rate with respect to time) using an ad hoc Couette shear cell. Tablets were compressed at different compaction forces using an instrumented compactor simulator, and compaction curves showing the force-displacement profiles during compaction...
30. March 2016
A pharmaceutical compound was used to study the effect of batch wet granulation process parameters in combination with the residual moisture content remaining after drying on granule and tablet quality attributes. The effect of three batch wet granulation process parameters was evaluated using a multivariate experimental design, with a novel constrained design space. Batches were characterised for moisture content, granule density, crushing strength, porosity, disintegration time and...
07. September 2015
There are many factors influencing the drug release behaviour from a pharmaceutical formulation as the particle size of the drug and excipient, porosity of the system or geometrical phase transitions of the components. Therefore, the choice of the adequate excipient to achieve a specific drug release profile is mainly based on the experience and the trial and error method. Taking into account the directives towards the application of the “Quality by Design” approach, in this study the...