- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
15. June 2018
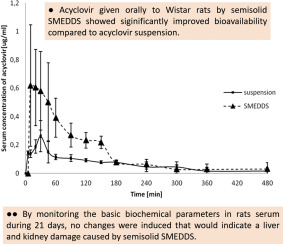
Semisolid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) with optimized drugloading capacity, stability, dispersibility in aqueous media and invitro drug release profile, was evaluated in vivo regarding effects on pharmacokinetics of acyclovir, an antiviral with low bioavailability (BA) and short half-life (t1/2). Additional goal of this study was evaluation of safety of this semisolid SMEDDS consisted of medium chain length triglycerides (oil) (10% w/w), macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate...
21. February 2017
Abstract: The aim of this work was to develop cefdinir solid dispersions (CSDs) prepared using hydrophilic polymers with enhanced dissolution/solubility and in vivo oral bioavailability. CSDs were prepared with hydrophilic polymers such as hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose (HPMC; CSD1), carboxymethylcellulose-Na (CMC-Na; CSD2), polyvinyl pyrrolidone K30 (PVP K30; CSD3) at the weight ratio of 1:1 (drug:polymer) using a spray-drying method. The prepared CSDs were characterized by aqueous solubility,...
23. January 2016
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are frequently used as an excipient to enhance the intestinal drug absorption of compounds with a low aqueous solubility. However, there exists an intricate interplay between opposing effects that determines the optimal dosing criterion. These opposing effects are the benefits of circumventing the dissolution time required to dissolve the non-absorbable drug particles in the intestine versus the disadvantage of decreasing the concentration of the drug available to permeate...
17. December 2015
The chemotherapeutic drug substance doxorubicin has been reported to be a substrate of P-gp, which induces a barrier for oral administration and leads to a bioavailability of 3% in male Sprague Dawley rats. Literature studies have reported increased transport of P-pg substrates, like digoxin, when co-administered with P-gp inhibitors (non-ionic surfactants) in vitro and in vivo. More