- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
29. September 2018
Appropriate lubrication is important in tablet manufacturing as it lowers punch sticking propensity and protects tooling by reducing friction between die wall and tablet during tablet manufacturing. Most commercial lubricants negatively impact tabletability and dissolution. A delicate balance is usually attained by trial and error to identify the optimal level of lubricant in a tablet formulation. In this work, we have evaluated the effectiveness of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), a surfactant, as...
13. August 2018
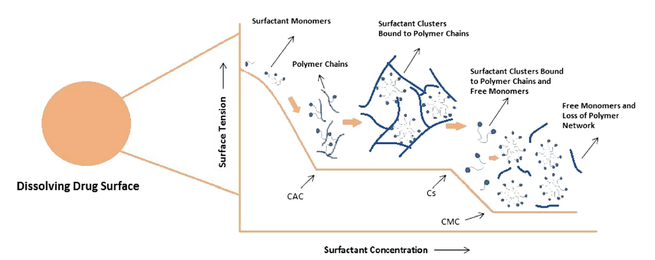
Surfactants are commonly incorporated in conventional and enabled formulations to enhance the rate and extent of dissolution of drugs exhibiting poor aqueous solubility. Generally the interactions between the drug and excipients are systematically evaluated, however, limited attention is paid towards understanding the effect of interaction between functional excipients and its impact on the performance of the product. In the current study, the effect of potential interaction between a nonionic...
15. February 2018
The poor oral bioavailability of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) resulting from low solubility is one of the important challenges in pharmaceutical technology. Over the last two decades the number of relatively insoluble drugs has grown steadily. Nowadays it is estimated that approximately 70% of new drug candidates are characterized by poor solubility.
11. December 2017
Nowadays most of the drug substances are coming into the innovation pipeline with poor water solubility. Here, the influence of excipients will play a significant role to improve the dissolution of poorly aqueous soluble compounds. The drug substance needs to be dissolved in gastric fluids to get the better absorption and bioavailability of an orally administered drug. Dissolution is the rate-controlling stage for drugs which controls the rate and degree of absorption.
24. November 2017
The aim of this new work was to improve the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble cilostazol (CLT) by adsorbing dissolved drug molecules onto the surface of undissolved carriers via reprecipitation and deposition process as the solvent (methylene chloride) was evaporated. The adsorption mixtures of CLT with Aerosil 300 and lactose monohydrate provided better drug dissolution rate as compared to mannitol.