- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
17. April 2018
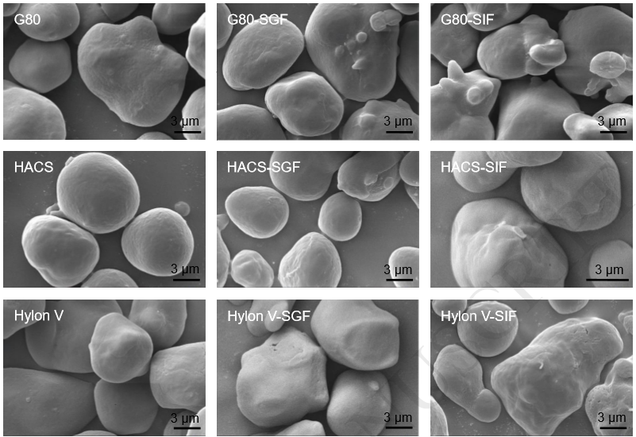
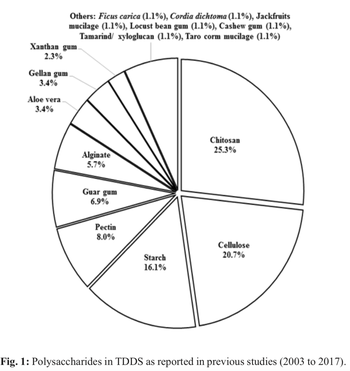
This article reviews various polysaccharides used in transdermal drug delivery system. The system provides continuous controlled delivery of active ingredients through human skin and into the blood stream. Poor penetration of most drugs into the skin has led to numerous studies being conducted to increase the permeability of such drugs. Currently, the interest to utilize natural polysaccharides in transdermal formulations has increased as an alternative to the synthetic materials. Structure...
19. March 2018
The aim of this study was to prepare and characterize a novel type of starch-coated microparticles (MPs) allowing site-specific delivery of bioactives to the colon. An oral colon-specific controlled-release system was developed in the form of MPs coated with a resistant starch (RS2/RS3) film (RS@MPs) through an aqueous suspension coating process.
05. March 2018
This study presents a framework for process and product development on a continuous direct compression manufacturing platform. A challenging sustained release formulation with high content of a poorly flowing low density drug was selected. Two HPMC grades were evaluated as matrix former: standard Methocel CR and directly compressible Methocel DC2. The feeding behavior of each formulation component was investigated by deriving feed factor profiles.
11. December 2017
Nowadays most of the drug substances are coming into the innovation pipeline with poor water solubility. Here, the influence of excipients will play a significant role to improve the dissolution of poorly aqueous soluble compounds. The drug substance needs to be dissolved in gastric fluids to get the better absorption and bioavailability of an orally administered drug. Dissolution is the rate-controlling stage for drugs which controls the rate and degree of absorption.
08. November 2017
Colon delivery systems for oral administration have grown in popularity since the 1990s, primarily because of the increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that has broadly been demonstrated to benefit from topical pharma- cological treatment.
08. November 2017
Co-processing is currently of interest in the generation of high-functionality excipients for tablet formulation. In the present study, comparative analysis of the powder and tableting properties of three co-processed starches prepared by three different methods was carried out. The co-processed excipients consisting of maize starch (90%), acacia gum (7.5%) and colloidal silicon dioxide (2.5%) were prepared by co-dispersion (SAS-CD), co-fusion (SAS-CF) and co-granulation (SAS-CG).
23. October 2017
The development of novel excipients with enhanced functionality has been explored using particle engineering by co-processing. The aim of this study was to improve the functionality of tapioca starch (TS) for direct compression by co-processing with gelatin (GEL) and colloidal silicon dioxide (CSD) in optimized proportions.
26. March 2017
Background Starchy products have been widely used in the food, paper, textile, plastic, cosmetics, adhesives, and pharmaceutical industries. To meet specific requirements of their applications, different modification techniques, such as physical, chemical, and enzymatic methods, have been employed to enhance or inhibit their inherent properties or to endow specific properties of starch. Scope and approach Debranched starch (DBS), modified by pullulanase or isoamylase, acquires remarkable new...
24. March 2017
Abstract. Starch is an economical excipient that is used in oral dosage form. It has poor compressibility and flowability. Pregelatinization and co-process as a physical modification technique have been conducted widely; nevertheless, the single modification shows a limitation. This study aims to assess and characterize the starch result of the modification of various tubers by a combination of modification methods. The starches from various tubers were extracted by sedimentation. Starch...
24. March 2017
Abstract: Orodispersible tablets (ODT) of levocetirizine was prepared using natural polysaccharides ipomoea batatas starch, amorphophallus campanulatus starch and their modified form by direct compression method and evaluated for their superdisintegrant activity. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride was used as a model drug. The prepared formulations were compared with synthetic superdisintegrants such as crosspovidone and diluent Ludiflash for disintegration and other ODT parameters. FTIR study...