- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
24. September 2017
Objective: The aim of present study was to prepare and evaluate the trans- dermal lms (TFs) of Nifedipine (NFDP). Methods: The TFs were prepared by solvent evaporation technique and twelve formulations of NFDPTFs were prepared by taking HPMC E15 and Eudragit L100 in different ratios. Polyethylene glycol (15%) and Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were incorpo- rated as plasticizer and permeation enhancer respectively. DMSO was in- corporated in the formulations F7-F12 but it was absent in F1-F6....
24. September 2017
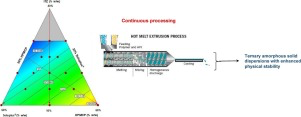
Abstract The aim of this study was to evaluate a novel combination of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP-HP-50) and Soluplus®polymers for enhanced physicochemical stability and solubility of the produced amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs). This was achieved using hot melt extrusion (HME) to convert the crystalline active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) into a more soluble amorphous form within the ternary systems. Itraconazole (ITZ), a Biopharmaceutics Classification System class...
07. September 2017
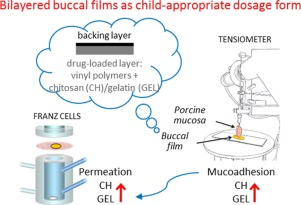
Abstract Buccal mucosa has emerged as an attractive site for systemic administration of drug in paediatric patients. This route is simple and non-invasive, even if the saliva wash-out effect and the relative permeability of the mucosa can reduce drug absorption. Mucoadhesive polymers represent a common employed strategy to increase the contact time of the formulation at the application site and to improve drug absorption. Among the different mucoadhesive dosage forms, buccal films are...
29. April 2017
Abstract Thoughtfully designed early clinical formulations not only meet the needs of the study at hand and inform the development of the commercial product, but can influence the direction of the clinical program as well as provide further guidance to potential backups still in exploratory stages. This chapter focuses on the various types of early clinical formulations, why they are developed, and how the preclinical formulation space helps to guide initial clinical formulation selection....
21. February 2017
Abstract The present investigation was undertaken with the objective of formulating Bufotenin for rapid dissolution of drug and absorption which may produce the rapid onset of action and also to improve the bioavailability of the drug. The fast dissolving strips were prepared by solvent casting method with the selection of HPMC E5, E15, K15, and Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC), Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) as polymers and glycerol as plasticizer. Prepared lms were carried out for in vitro...
16. February 2017
Abstract Spironolactone is a drug derived from sterols that exhibits an incomplete oral absorption due to its low water solubility and slow dissolution rate. In this study, formulations of spironolactone with four disintegrants named as croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, sodium starch glycolate and microcrystalline cellulose II (MCCII) were conducted. The effect of those disintegrants on the tensile strength, disintegration time and dissolution rate of spironolactone-based compacts was...
14. February 2017
Abstract 5w?>The morbidity and mortality toll of pediatric cancer affects the public health of children worldwide, but despite the gains in the fight against cancer, more progress needs to take place against this disease, which is a leading cause of death and chronic disability in children. In response, leading regulatory authorities in the developed world have been ratcheting up their efforts to induce the private sector to expand their research and development focus during drug development...
30. September 2016
ABSTRACT Oral dosage form is the physical form of a dose of a chemical compound used as a drug or medication intended for administration or consumption by the oral route. The poor dissolution rate of water insoluble drugs is still a substantial problem confronting the pharmaceutical industry. There are several methods used to increase the solubility of drugs, of those liquid-solid compact (LSC) technique is a new and promising addition towards such a novel aim, that the solubility of the...
18. July 2016
OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to determine the influence of non-ionisable excipients hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) and poloxamers 407 and 188 on the supersaturation and precipitation kinetics of ibuprofen, gliclazide, propranolol and atenolol induced through solution pH shifts using the CheqSol method. METHODS: The drug's kinetic and intrinsic aqueous solubilities were measured in the presence of increasing excipient concentrations using the CheqSol method. Experimental data...
06. May 2016
The aim of present study was to develop the Lacidipine oral disintegrating tablets (LCDP ODTs), thereby enhancing the solubility and dissolution rate. Solubility was enhanced by solid dispersion technology using hydrophilic carriers like Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose Acetate Succinate (HPMCAS), β-Cyclodextrin BCD), Polyethylene Glycol 6000 (PEG 6000) and it was confirmed by phase solubility studies. LCDP ODTs were prepared by using super disintegrants like Croscarmellose Sodium (CCS),...