- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. December 2017
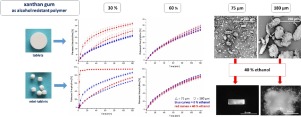
The vulnerability of controlled release formulations when co-ingested with alcohol represents a current major concern of regulatory agencies. Dose dumping might occur when drugs and/or excipients exhibit higher solubility in ethanolic solutions compared to water.
12. December 2017
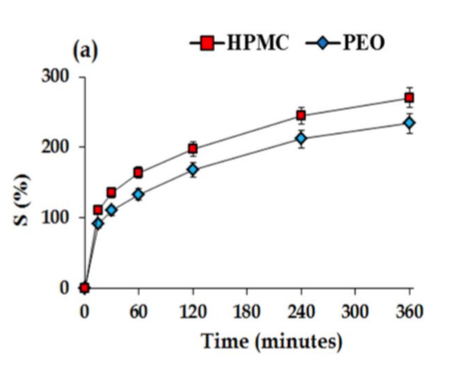
The aim of the present investigation was to understand the swelling behaviour of HPMC and PEO-based matrices and to evaluate the impact of porosity on the swelling kinetics. It was noticed that the HPMC has higher swelling rates but both undergo diffusion oriented swelling mechanism.
07. September 2017
Abstract Purpose: To formulate and evaluate an antispasmodic drug, mebeverine hydrochloride (Mbv-HCl), as a local anesthetic mucoadhesive buccal tablet. Methods: Mbv-HCl loaded tablets were formulated, using a direct compression technique, with varying polymer concentrations including carbopol 934P alone, carbopol 934P/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) mixture, or carbopol 934P/chitosan mixture. The tablets were evaluated for physicochemical characteristics, in-vitro drug release,...
23. May 2017
The performance of a drug is primarily influenced by the disintegration and dissolution behaviour of the powder compact.
27. February 2017
Abstract: The main challenges facing efforts to prevent the transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are the lack of access to sexual education services and sexual violence against young women and girls. Vaginal formulations for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections are currently gaining importance in drug development. Vaginal mucoadhesive tablets can be developed by including natural polymers that have good binding capacity with mucosal tissues, such as chitosan or guar...
23. January 2017
Abstract This study has investigated the potential use of zein protein from corn as a pharmaceutical excipient for formulation of oral controlled-release matrices. SMCC (silicified microcrystalline cellulose)-Prosolv® 90, SMCC HD-Prosolv® 90 HD, Avicel® PH 102 and Mannitol 60 were evaluated as co-excipients to improve the processability of zein powder. Zein/SMCC-Prosolv® 90 blend had the best flowability and tabletability. Tablets with tramadol hydrochloride, zein and SMCCProsolv® 90 were...
14. December 2016
Topical hydrogel preparations are applied on skin to obtain local or systemic action. NSAID’s are non-steroidal drugs having excellent anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity but it produces GIT ulceration when used orally. To overcome that problem with oral formulations, many NSAID’s are preferred to be administered by topical route. The present investigation is aimed to formulate the hydrogel of Diclofenac potassium with different ratio of Carbopol of different grades along with guar gum...
18. October 2016
Abstract The objectives of the present study were to develop a controlled-release bilayered tablet of aceclofenac (AFN) 200 mg with dual release and to gain a mechanistic understanding of the enhanced sustained release capability achieved by utilizing a binary mixture of the sustained release materials. Different formulations of the sustained-release layer were formulated by employing hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) as the major retarding polymers. The in...
26. September 2016
Abstract Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-based hot melt extrudates offer an interesting potential as oral controlled drug delivery systems and can provide additional advantages, such as reducing the risk of drug abuse. Different polymer molecular weight PEOs are commercially available and can be used to prepare drug-loaded hot melt extrudates. Importantly, the macromolecular chain length impacts crucial system features, including the swelling and erosion kinetics of the systems, which determine the...
20. June 2016
ABSTRACT Objective: The objective of the work is to formulate gliclazide bioadhesive tablets that will significantly improve the availability of the drug especially under the situations of prolonged use of drug and also reduce the total dosage of administered drug and consequently reduce the side effects. All these factors will ultimately lead to enhanced patient compliance and patient care. Methods: Various natural and semi synthetic polymers were screened and they were selected on the basis...