- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
08. July 2018
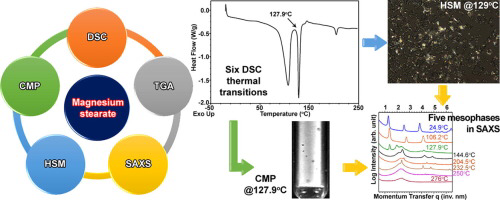
Magnesium stearate (MgSt) is the most commonly used excipient for oral solid dosage forms, yet there is significant commercial physicochemical variability that can lead to variable performance of critical product attributes. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is often used as a quality control tool to characterize MgSt, but little data is available regarding the physicochemical relevance for the DSC thermograms. The main aim of this study was to decipher MgSt’s complex thermotropic...
16. September 2017
Abstract We aimed to understand the factors controlling mechanical particle coating using polymethacrylate. The relationship between coating performance and the characteristics of polymethacrylate powders was investigated. First, theophylline crystals were treated using a mechanical powder processor to obtain theophylline spheres (<100 μm). Second, five polymethacrylate latexes were powdered by spray freeze drying to produce colloidal agglomerates. Finally, mechanical particle coating was...
11. April 2017
Abstract Ribavirin (C8H12N4O5; anti-viral agent) was crystallized as two unique, phase-pure polymorphs (R-I and R-II). Calorimetrically determined isobaric heat capacities and heat of transition data were utilized to determine the solid-state transition temperature (Ttr), confirming enantiotropism, while R-I was determined to be kinetically stable at ambient temperature. Unprocessed samples of the low Tm polymorph, R-II, did not convert into R-I when held isothermally well above Ttr for 7 days....
30. August 2016
Abstract In situ -gelling systems has the great potential in the wide areas of drug delivery. The application areas of such systems are broad and these systems can be formulated not only as gels but also as in situ gelling nanospheres, microspheres and liposomes. To overcome the drawbacks associated with conventional drug delivery systems and take advantages of both solutions and gels, such as accurate dosing, ease of administration of the former and longer precorneal residence of the latter, a...
25. June 2016
Abstract A facile controlled-release nanogels delivery system has been developed by using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) hybrid nanogels as encapsulation shell materials, which were synthesized by surfactant-free polymerization in aqueous solution. The effects of reaction time and cross-linker concentration on the size of the nanogels have been studied. The results showed that in a certain range, the particle size decreased with increasing reaction time and increasing concentration of...
14. April 2016
In this study, the effect of the incubation time, incubation temperature, pH, metal and sodium ions on the antibacterial activity of chitosan against food borne spoilage bacteria focused. Aeromonas hydrophila and Staphylococcus aureus, were used as two food borne bacteria. Acetic acid was used dissolving of chitosan. Results showed that chitosan solution at 5 mg/mL significantly inhibited the growth of A. hydrophila and S. aureus in presence of time, pH and metal ions (p <0.01). However,...
05. March 2016
Solubility parameters of HPMCAS have not yet been investigated intensively. On this account total and three dimensional solubility parameters of HPMCAS were determined by using different experimental as well as computational methods. In addition, solubility properties of HPMCAS in a huge number of solvents were tested and a Teas plot for HPMCAS was created. The total solubility parameter of about 24 MPa0.5 was confirmed by various procedures and compared with values of plasticizers. 20 common...
05. December 2015
15. September 2015
Hot-melt extrusion technology has been widely reported for producing amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble compounds. A number of studies revealed that enteric polymers containing ionizable groups are able to improve the physical stability and maintain drug supersaturation, thereby enhancing oral bioavailability. More
06. September 2015
Objective of this work was to understand the mechanism of formation of celecoxib nanocrystals in celecoxib: mannitol nanocrystalline solid dispersion (NSD). Solution of celecoxib and mannitol was spray dried in 1:1 (g:g) proportion to obtain NSD, with average crystallite size of 214.07 ± 45.27 nm. Solubility parameters of celecoxib and mannitol were 23.1 MPa1/2 and 38.5 MPa1/2, respectively, hinting their immiscibility. More