- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
The aim of this work was to develop an ascending controlled-release pellet (ACRP) of paliperidone to improve poor solubility and provide a stable blood drug concentration. The inner core was produced by mixing different ratios of sodium chloride as an osmotic substance and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) to offer a pressure drive when in contact with medium. After, the drug layer was processed by a liquid-layering method, with paliperidone ground to a nano-size in order to improve the...
08. July 2018
The purpose of this study was to develop self-microemulsifying (SME-) tablets to improve resveratrol solubility whilst delivering resveratrol in a preferred tablet dosage form. Resveratrol was dissolved in liquid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) (10 % w/w) and solidified through adsorption on several different solid carriers. Two ranges of synthetic amorphous silica (Sylysia® 290, 350, 470, 580; Syloid® 244FP, AL-1FP) as well as granulated magnesium aluminometasilicate...
06. May 2018
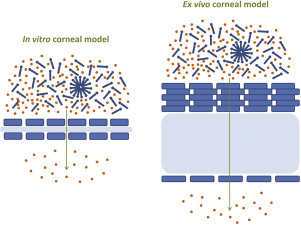
The objective of this study was to systematically investigate the effects of surface active ophthalmic excipients on the corneal permeation of ophthalmic drugs using in vitro(HCE-T cell-based model) and ex vivo (freshly excised porcine cornea) models. The permeation of four ophthalmic drugs (i.e., timolol maleate, chloramphenicol, diclofenac sodium and dexamethasone) across in vitro and ex vivocorneal models was evaluated in the absence and presence of four commonly used surface active...
26. March 2018
A novel hybrid microparticulate system composed of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles and submicron medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) droplets was fabricated to overcome the pH-dependent solubility and precipitation challenges associated with a model poorly water-soluble weak base, cinnarizine (CIN). Molecular CIN was confined within both the lipid and polymer phase of PLGA-lipid hybrid (PLH) and PLGA-lipid-mannitol hybrid (PLMH) particles, which offered significant...
26. October 2017
Mycotoxins are secondary toxic metabolites that are produced by fungi representing threats to human and animal health. The objective of this study was to evaluate the adsorption capacity of Chitosan (CHI), and three cellulosic polymers (HPMC, CMC, and MCC), on six mycotoxins (AFB1; FUB1; OTA; T-2; DON; and, ZEA) using an in vitro digestive model for poultry. The adsorbent capacity of the materials in the supernatant of each compartment was evaluated by a non-competitive chemiluminescent assay....
07. October 2017
Polymer based dosages form the mainstay of drug delivery systems either as simple matrix carrier materials or active release behaviour modulating agents. In addition, several techniques have been developed further to deliver novel polymeric structures. One such method is electrospinning (ES); a maturing process which is operational at the ambient environment and enables drug loading (in molecularly dispersed form) directly into a fibrous polymer matrix system. Since there is an impending need...
15. March 2017
Abstract The present study was designed to prepare and compare bio-adhesive pellets of panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) with hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), chitosan, and chitosan : carbomer, explore the influence of different bio-adhesive materials on pharmacokinetics behaviors of PNSbio-adhesive pellets, and evaluate the correlation between in vivo absorption and in vitro release (IVIVC). In order to predict the in vivo concentration-time profile by the in vitro release data of...
03. March 2017
Abstract A 23 Factorial design of cissus-gelatin B polymer blends was developed to formulate amodiaquine HCl-artesunate (AQ-AS) microparticles by varying the polymer blend concentration (2 %w/v, 5 %w/v), crosslinking time (0.5 h, 1 h) and glutaraldehye volume (0.5 ml, 1 ml). The formulations were evaluated using drug entrapment efficiency (EE), particle size, polydispersity index, thermal behaviour with differential scanning calorimetry, crystallinity with powder X-ray diffraction, morphology...
10. February 2017
Purpose To develop a model linking in vitro and in vivo erosion of extended release tablets under fasting and postprandial status. Methods A nonlinear mixed-effects model was developed from the in vitro erosion profiles of four hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) matrix tablets studied under a range of experimental conditions. The model was used to predict in vivo erosion of the HPMC matrix tablets in different locations of the gastrointestinal tract, determined by magnetic marker monitoring....
06. February 2017
Abstract Liquid adsorption on solid adsorbent carriers is an emerging technique for oral lipid-based drug delivery systems. The purpose of the current study is to convert liquid into solid self-emulsifying lipid formulations (SELFs) using an inorganic adsorbent Neusilin® grade US2 (NUS2) and investigate in vitro dissolution and digestion performance of the model antipsychotic compound risperidone. Methods The liquid SELFs were designed using various oils, nonionic surfactants and converted...