Anisotropic features with other crystallographic properties like d-spacing,and
attachment energy (Eatt) can predict material performance during the secondary pharmaceutical processing. A newly developed state-of-the-art compression cell lodged
in apowder X-ray diffractometer was used to measure anisotropic Young’s moduli (YM) of flufenamic acid (FFA) polymorphs in this study. Methodology is based on the generation of a single
crystal deformation in this cell, which reflects as a change
in the d-spacing inthe PXRD pattern. Anisotropic YM was calculated from such information gathered along different FFA planes. Measured FFA crystallographic molecular features were concatenated to
understand macroscopiccompaction (Heckel and Shapirao’s parameters) and tableting performance. Block shaped crystals of FFA form I, and IIIafter initial characterization with SEM, DSC,
PXRD, and FTIR were compressed normal to X, Y, and Z-planes, identified fromcalculated PXRD pattern using
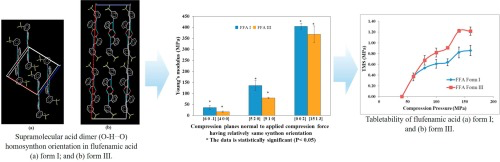
the reported single crystal structure. YM of X and Y planes of form I was significantly higher than corresponding planes of form III. Z plane of form III showedsignificantly higher YM than that
for form I. Low YM of form III can be attributed to its large d-spacing regardless of their high Eatt than form I, as well as orientation
of supramolecular acid dimer (OH⋯O) homosynthon chains in the FFAplanes. FFA form I
stiffness was further confirmed with lower densification and higher yield pressure of deformation than form III. Clearly, form III exhibited better compressibility, compactibility,and tableting
performance than form I due to favorable molecular and macroscopic features. Thus, developed anisotropic measurement approach can be used to distinguish material performance in theearly
development stage of the pharmaceutical processes.