- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
16. August 2018
Vaginal drug delivery is a promising route for the treatment and prevention of local and systemic diseases such as genital herpes or AIDS. Suitable excipients must be selected to optimize the residence time of formulations in vaginal mucosa and could be included in the formulation. Many polymers are excellent choices for the development of vaginal drug delivery systems due to their properties of mucoadhesion, biocompatibility and biodegradability. These polymers swell in the aqueous medium of...
07. July 2018
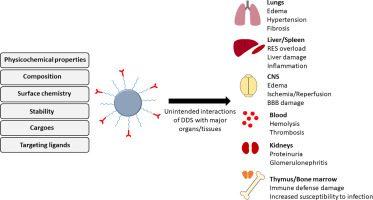
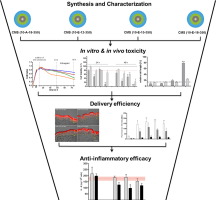
Humoral and cellular host defense mechanisms including diverse phagocytes, leukocytes, and immune cells have evolved over millions of years to protect the body from microbes and other external and internal threats. These policing forces recognize engineered sub-micron drug delivery systems (DDS) as such a threat, and react accordingly. This leads to impediment of the therapeutic action, extensively studied and discussed in the literature. Here, we focus on side effects of DDS interactions with...
11. January 2018
Aqueous pharmaceutical solutions provide prosperous living conditions for microbiological agents. In order to eliminate these microbes, we use preservatives which can harm human cells as well. Their cytotoxicity is concentration-dependent and the aim of our study was to find how other pharmaceutical excipients modify the cytotoxic attributes of preservatives. We tested the following compounds: methylparaben, benzalkonium chloride, polysorbate 20, Labrasol® and hydroxyethyl cellulose. T
31. October 2017
Drug loaded dendritic core-multishell (CMS) nanocarriers are of especial interest for the treatment of skin diseases, owing to their striking dermal delivery efficiencies following topical applications. CMS nanocarriers are composed of a polyglycerol core, connected by amide-bonds to an inner alkyl shell and an outer methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) shell.
27. July 2016
Development of new products and materials, especially those which are based on renewable organic resources using innovative sustainable processes, represents an increasing interest in both academic and industrial research. Cellulose and its derivatives have demonstrated to be versatile materials with unique chemical structure which provides a good platform for the construction of hydrogel networks with distinctive properties as respects of swelling ability and sensibility to external stimuli....
20. June 2016
Abstract Since the discovery about 30 years ago (2-hydroxypropyl) beta-cyclodextrin, a highly soluble derivative of beta-cyclodextrin, has become an approved excipient of drug formulations included both in the United States and European Pharmacopoeias. It is recommended to use as solubilizer and stabilizer for oral and parenteral formulations. Recently, its pharmacological activity has been recognized in various diseases. The increasing applications require a closer look to the...
29. February 2016
The development of novel biomedical materials for practical and clinical applications, such as drug carriers, biocompatible tissue or organ substitute materials, repair and regeneration biomaterials, etc., is always a most concerned topic for biologists and material scientists. Many natural materials have been used as biomedical materials to replace traditional organic synthetic materials. More
20. October 2015
05. June 2015
Highlights •Novel BC composites with improved mechanical integrity. •Sustained in vitro release of the antibiotic (levofloxacin) from the BC composites over an 8-week period. •Levofloxacin retained the antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis over an 8-week in vitro release period. •Biocompatible BC composites. See more