- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
01. August 2018
Advancements in in silico techniques of lead molecule selection have resulted in the failure of around 70% of new chemical entities (NCEs). Some of these molecules are getting rejected at final developmental stage resulting in wastage of money and resources. Unfavourable physicochemical properties affect ADME profile of any efficacious and potent molecule, which may ultimately lead to killing of NCE at final stage. Numerous techniques are being explored including nanocrystals for solubility...
01. March 2018
Most of antibacterial and antiviral agents and drugs for the treatment of central nervous system and cancer are water-insoluble, which reduces their bioavailability. The bioavailability of substances can be increased by using a dosage form such as nanosuspension.
09. January 2018
The effective surface area of drug particle is increased by a reduction in the particle size. Since dissolution takes place at the surface of the solute, the larger the surface area, the further rapid is the rate of drug dissolution. Ketoprofen is class II type drug according to (Biopharmaceutics Classification System BCS) with low solubility and high permeability.
05. December 2017
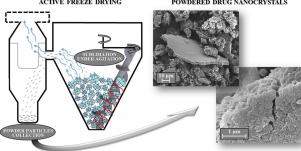
Active Freeze Drying allows for producing lyophilised powders by progressive agitation of frozen blocks undergoing sublimation. One potential application of this process is the formulation design of unstable nanosuspensions for oral drug delivery, as here shown for nanocrystal-based ketoconazole powder.
27. November 2017
Drug solubility can pose a great challenge for the development of novel formulations and impacts a wide spectrum of drugs with poor solubilities. Drug efficacy is known to be proportionally related to the solubility of a drug. Poor solubility of a drug leads to low dissolution rate and in turn to low absorption in the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Pharmaceutical particle technology is often used to improve poor aqueous solubility of drug compounds that limits in vivo bioa
12. October 2017
Poor aqueous solubility leading to poor oral bioavailability is a bottle neck in the development of many new drug candidates; particularly the BCS class II-IV drugs. These molecules are difficult to formulate using conventional approaches and are associated with numerous formulation related performance issues.
24. July 2017
The development of nanosuspensions of poorly soluble APIs takes a lot of time and high amount of active material is needed. In this publication the use of dual centrifugation (DC) for an effective and rapid API-nanomilling is described for the first time.
06. April 2017
Abstract A stabilized high drug load intravenous formulation could allow compounds with less optimal pharmacokinetic profiles to be developed. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-ylation is a frequently used strategy for particle delivery systems to avoid the liver, thereby extending blood circulation time. The present work reports the mouse in vivo distribution after i.v. administration of a series of nanocrystals prepared with the bead milling technique and PEG-ylated with DSPE-PEG2000 and Pluronic...
10. July 2016
A cationic nanocrystal formulation containing dexamethasone acetate nanocrystals (0.05%) and polymyxin B (0.10%) for ophthalmic application was produced using a self-developed small scale method for wet bead milling. The formulation developed offers the advantage of increased saturation solubility of the drug (due to the nano-size of the crystals), increased residence time in the eye (due to small size and increased mucoadhesion by the cationic charge) resulting ultimately in potential...
24. February 2016
Cinnarizine (CIN), a poorly soluble drug with erratic bioavailability due to pH dependent solubility has limited advantage to formulate oral solid dosage forms in subject having low gastric acidity. In present study precipitation-ultrasonication was used to fabricate nanosuspensions of cinnarizine stabilized by Poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) to enhance the bioavailability. We investigated the effects of PVA concentration (X1) and solvent to antisolvent ratio (X2) on the quality attributes like mean...