- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
14. December 2017
Purpose Artificial tears are widely used in the treatment of dry eye disease, although current formulations do not closely resemble natural tears. The purpose of this study was the design and characterization of a novel in situ gelling artificial tear formulation, containing both lipid and aqueous components, in order to resemble natural tears and replenish the tear film. Methods Liposomes, containing phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol, vitamins A and E, were prepared by the thin-film hydration...
05. September 2017
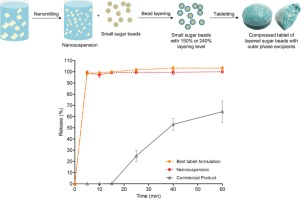
Abstract There has been limited research done on the downstream processing of nanosuspensions into solid oral dosage forms. This paper demonstrates the bead layering process with a layering level at 150% and 240%, as well as the selection and justification of the outer phase excipients for tabletability and disintegrating properties. In a previous study, an itraconazole nanosuspension stabilised by SDS and HPMC E5 was layered onto sugar beads with coating polymer HPMC VLV. In the current study,...
24. August 2017
Chemotherapy is one of the most conventionally used therapeutic interventions for treating various diseases. Chances of acquiring multidrug resistance in response to chemotherapeutic agents are exceedingly common among patients
18. April 2017
Abstract There is more research required to broaden the knowledge on the downstream processing of nanosuspensions into solid oral dosage forms, especially for coated nanosuspensions onto beads as carriers. This study focuses on bead layering as one approach to solidify nanosuspensions. The aim was to systematically investigate the influence of type of coating polymer (HPMC VLV vs. copovidone), bead material and bead size (sugar vs. MCC, and small vs. large) and coating thickness (50%–150%...
30. March 2017
Abstract Chitin is one of the most abundant natural polymers in the world and is used for the production of chitosan by deacetylation. Chitosan is nontoxic and biodegradable and, therefore, can be used as a biomaterial and for the construction of drug delivery systems. Nevertheless, the poor solubility of chitosan in neutral or alkalinized media has restricted its applications in the pharmaceutical and biomedical fields. Chitosan can be easily carboxymethylated to improve its solubility in...
01. October 2016
Abstract Current polymeric research has explored various applications in drug delivery and its related biomedical applications. Natural polymers especially those are derived from plant sources has evidenced for growing interest and attention in biomedical and pharmaceuticals sectors. Owing to their relative abundance, low cost, and biodegradable and eco-friendly profiles, plant derived polysaccharides are more preferred over the synthetic polymers. Present work demonstrates the drug delivery...
30. September 2016
Abstract Combining two or more antiretroviral drugs in one medical product is an interesting but challenging strategy for developing topical anti-HIV microbicides. We developed a new vaginal delivery system comprising the incorporation of nanoparticles (NPs) into a polymeric film base – NPs-in-film – and tested its ability to deliver tenofovir (TFV) and efavirenz (EFV). EFV-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) NPs were incorporated alongside free TFV into fast dissolving films during film...
18. September 2016
Abstract: Background: Amphotericin B eye drops are widely used in the treatment of ocular infections. However, amphotericin’s toxicity leads to low patient compliance and aggravation of symptoms. This work describes the development of a microemulsion system containing amphotericin B, aiming for its use in ocular applications. Methods: The microemulsion was developed by the titration technique. The physicochemical characteristics were determined with both loaded and unloaded amphotericin...
24. July 2016
Objectives Carvedilol (CAR) is a poorly water-soluble beta-blocker. Its encapsulation within nanomicelles (NMs) could improve drug solubility and its oral bioavailability, allowing the development of a paediatric liquid CAR formulation with commercially available copolymers: D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) and poly(vinyl caprolactam)-poly(vinyl acetate)-poly(ethylene glycol) (Soluplus®). Methods Drug-loaded NMs were prepared by copolymer and CAR dispersion in...
30. June 2016
Abstract: In HIV-1 management, eradication of the virus from sanctuaries represents a major and challenging goal. The genital tract, gut associated lymphoid tissue, lymph nodes, central nervous system, macrophages and latently infected CD4+ T lymphocytes are typical sites where HIV-1 compartmentalizes. To circumvent this problem, a consistent number of studies have focused on improving ARVs (antiretroviral drugs) delivery into sanctuary sites and different nanotechnological approaches have been...