- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
08. August 2018
Combinatorial chemistry, computational molecular modeling and high throughput screening in drug discovery have significantly increased the number of poorly soluble drugs. About 40% of drugs developed in the past and about 90% of the drugs in development are poorly soluble drugs. When administered orally, a drug has to first dissolve in gastrointestinal fluids before it can be absorbed in to the blood and reach its site of action. The objective of this review article is to outline the key...
30. May 2018
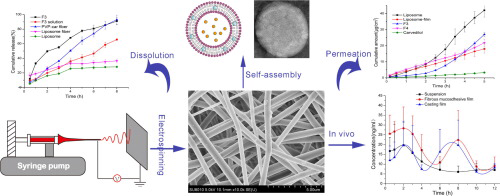
A novel delivery system based on self-assembled liposome from multi-layered fibrous mucoadhesive membrane has been developed to improve the bioavailability of Carvedilol (Car). This system consisted of an electrospun layer (enable self-assembly of liposome once contacting with water), an adhesive layer (prolong the retention period in the mouth) and a backing layer . SEM、 DSC and FTIR were applied to characterize the fiber. The TEM and fluorescence study demonstrated the formation of...
21. May 2018
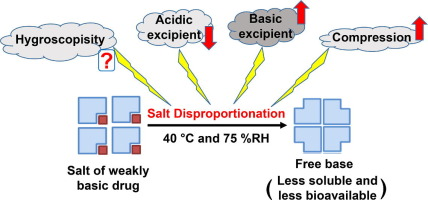
Excipients are crucial components of most pharmaceutical formulations. In the case of a solid oral dosage formulation containing the salt form of a weakly ionizable drug, excipient selection is critical, as some excipients are known to cause salt disproportionation (conversion of salt to the free form). Therefore, robust formulation design necessitates an in-depth understanding of the factors impacting salt disproportionation during processing or storage as this can negatively impact product...
09. March 2018
The use of amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) to overcome poor drug solubility has gained interest in the pharmaceutical industry over the past decade. ASDs are challenging to formulate because they are thermodynamically unstable, and the dispersed drugs tend to recrystallize. Until now, most research on ASDs has focused on immediate-release formulations, supersaturation, and stability; only a few studies have recently reported on the manufacturing of sustained-release ASDs.
19. February 2018
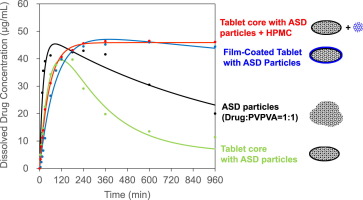
The effects of tablet preparation and subsequent film coating with amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) particles that were composed of a drug with poor water solubility and hydrophilic polymers were investigated. ASD particles were prepared with a drug and vinylpyrrolidone–vinyl acetate copolymer (PVPVA) or polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) at a weight ratio of 1:1 or 1:2 using a melt extrusion technique. Tablets were prepared by conventional direct compression followed by pan coating. A mathematical...
15. February 2018
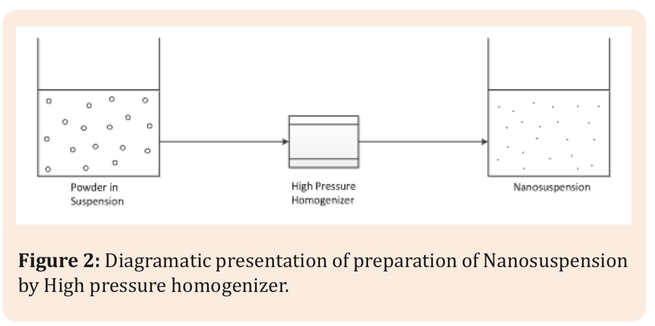
The poor oral bioavailability of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) resulting from low solubility is one of the important challenges in pharmaceutical technology. Over the last two decades the number of relatively insoluble drugs has grown steadily. Nowadays it is estimated that approximately 70% of new drug candidates are characterized by poor solubility.
26. January 2018
The understanding of amorphous solid dispersions has grown significantly in the past decade. This is evident from the number of approved commercial amorphous solid dispersion products. While amorphous formulation is considered an enabling technology, it has become the norm for formulating poorly soluble compounds.
11. January 2018
The oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can be improved by the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) where the API is dissolved in polymeric excipients. Desired properties of such ASDs like storage stability, dissolution behavior, and processability can be optimized by additional excipients. In this work, the influence of so-called low-molecular-weight excipients (LMWEs) on the phase behavior of ASDs was investigated.
24. December 2017
The preparation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) is a well-established strategy for formulating active pharmaceutical ingredients by embedding them in excipients, usually amorphous polymers. Different polymers can be combined for designing ASDs with desired properties like an optimized dissolution behavior.
06. November 2017
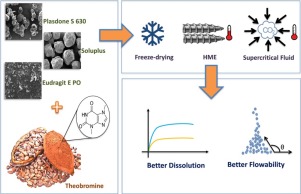
The aim of this study was to improve the pharmaceutical properties of theobromine (TB), particularly its flowability and dissolution rate, by preparing solid dispersions using different technologies (hot melt extrusion—HME, freeze-drying—FD, and supercritical fluid—SF) as well as testing different hydrophilic polymeric matrixes (Eudragit™ E, Plasdone™ S and Soluplus™)